Some of the most important events on an economic calendar
An economic calendar is a crucial tool for investors, traders, and analysts as it provides a schedule of significant economic events and announcements that can impact financial markets.
Table of Contents
1. Introduction
2. Understanding Economic Calendars
3. Key Economic Indicators
4. Impact of Economic Events
5. Major Central Bank Announcements
6. Economic Data Releases
7. Geopolitical Events and Their Impact
8. Natural Disasters and Economic Consequences
9. Corporate Earnings Reports
10. Industry-Specific Events
11. Global Economic Summits
12. Black Swan Events
13. Economic Calendar Tools
14. Analyzing and Utilizing Economic Calendars
15. Economic Calendar and Personal Finance
16. The Future of Economic Calendars
17. Tips for Using Economic Calendars Effectively
18. Common Mistakes to Avoid with Economic Calendars
19. Case Studies of Market Reactions
20. The Role of Media in Reporting Economic Events
21. Regulatory Changes and Economic Calendars
22. Economic Calendar and International Trade
23. How Economic Calendars Shape Public Policy
24. Understanding Market Volatility
25. Conclusion
Introduction
An economic calendar is a vital tool used by traders, investors, businesses, and policymakers to stay informed about significant economic events. It provides valuable insights into the economic health of a country or region, aiding in making informed decisions. This article will explore some of the most crucial events on an economic calendar and their impact on financial markets and various sectors of the economy.
Understanding Economic Calendars
2.1 What is an Economic Calendar?
An economic calendar is a schedule of key economic events, data releases, and announcements that are expected to occur over a specific period. It includes a wide range of events, such as central bank meetings, economic indicators, corporate earnings reports, geopolitical events, and more. These calendars are used by financial professionals, traders, investors, and economists to track important events that may impact the financial markets and the overall economy.
An economic calendar typically displays the date and time of each event, along with the country or region to which the event is related. It also provides a brief description of the event and the anticipated impact it might have on the economy or the markets. Economic calendars are available in various formats, including online platforms, financial news websites, and trading platforms.
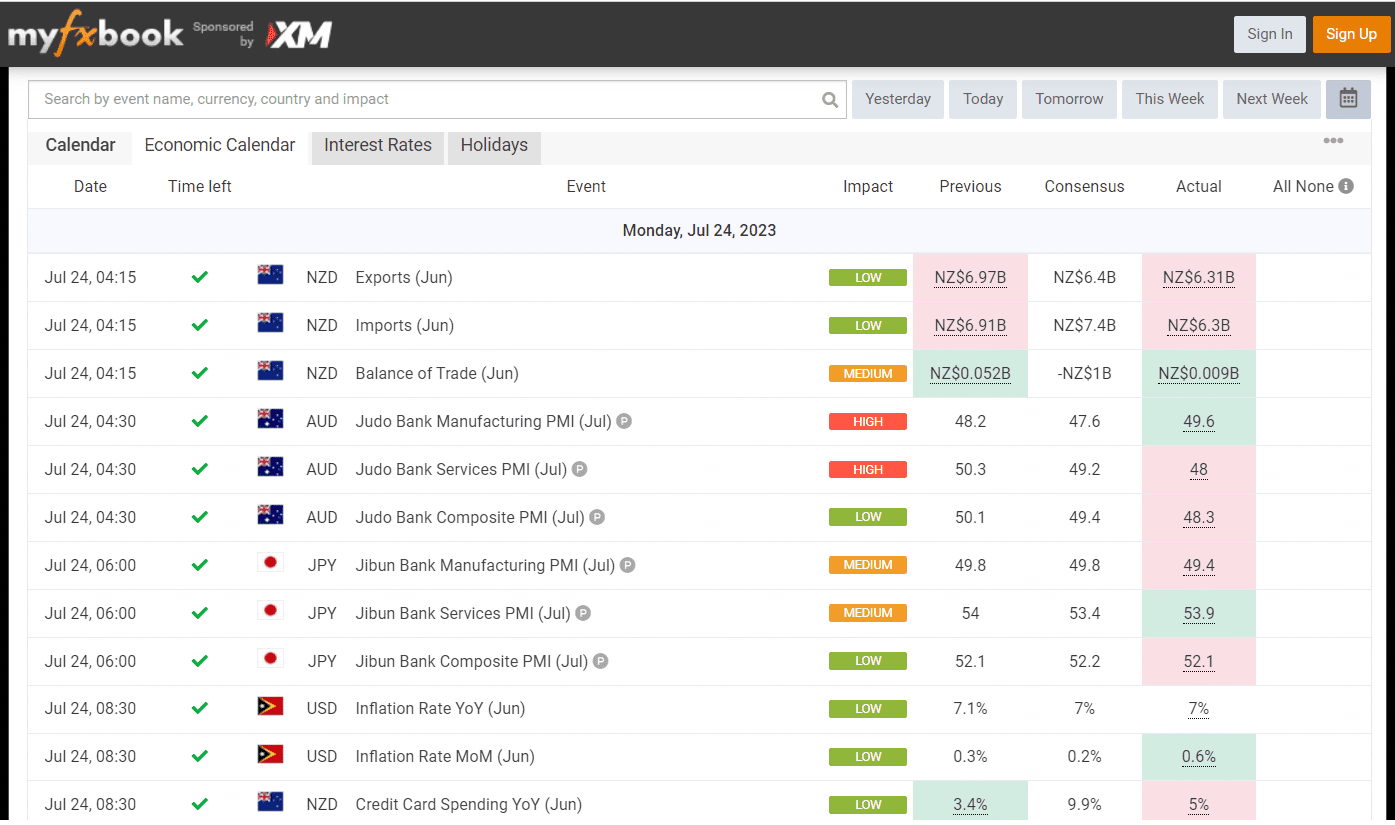
Image source from myfxbook
2.2 Why are Economic Calendars Important?
Economic calendars play a crucial role in the financial world for several reasons:
- Market Sentiment and Volatility: Economic events can significantly impact market sentiment and volatility. Traders and investors closely monitor economic calendars to prepare for potential market fluctuations and to adjust their strategies accordingly.
- Policy and Investment Decisions: Policymakers and businesses use economic calendars to make informed decisions. For example, a central bank might decide to adjust interest rates based on the latest economic data.
- Forecasting Economic Trends: By analyzing past and upcoming economic events, economists and analysts can forecast future economic trends and identify potential risks and opportunities.
- Global Economic Monitoring: Economic calendars provide a comprehensive view of economic events across different countries and regions, allowing for a global perspective on economic developments.
- Maximizing Opportunities: Traders and investors can use economic calendars to identify potential trading opportunities. For instance, a positive economic report might signal a favorable time to invest in certain assets.

3. Key Economic Indicators
3.1 Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
GDP is one of the most critical economic indicators and measures the total value of goods and services produced within a country's borders during a specific period. It serves as a barometer of a nation's economic health and growth. Changes in GDP can signal the beginning of economic expansions or contractions.
3.2 Consumer Price Index (CPI)
The CPI is a measure of the average change in prices of a basket of goods and services commonly purchased by households. It is used to track inflation trends, which can impact purchasing power and the overall cost of living.
3.3 Unemployment Rate
The unemployment rate represents the percentage of the labor force that is unemployed and actively seeking employment. A low unemployment rate is generally seen as a positive indicator of economic health.
3.4 Interest Rates
Central banks use interest rates as a tool to control inflation and stimulate or slow down economic activity. Changes in interest rates can influence borrowing and spending behavior.
3.5 Retail Sales
Retail sales data provides insights into consumer spending patterns, which is a significant driver of economic growth. Strong retail sales figures indicate a robust economy.
4. Impact of Economic Events
4.1 How Economic Events Influence Financial Markets
Economic events can trigger significant movements in financial markets, such as stock exchanges, forex markets, and commodity markets. The release of key economic data or announcements can lead to heightened volatility and sudden price fluctuations. For example, a better-than-expected GDP growth rate may result in a surge in stock prices, while a disappointing employment report could lead to a market sell-off.
Traders and investors closely monitor economic events to capitalize on market movements. They may adjust their positions, buy or sell assets, or hedge their portfolios based on the anticipated outcomes of these events. As a result, economic calendars are invaluable tools for anyone involved in financial markets, as they help individuals stay well-informed and make timely decisions.
4.2 Effects on Business and Investment Decisions
Economic events can also have a profound impact on businesses and their investment decisions. For instance, an interest rate hike by the central bank might lead to increased borrowing costs for businesses, affecting their expansion plans or investment in new projects. On the other hand, a favorable economic outlook might encourage businesses to take calculated risks and invest in growth opportunities.
Uncertainty surrounding economic events can lead to cautious decision-making by businesses. For instance, during times of economic volatility, companies may delay capital expenditures, hiring, or expansion plans until there is more clarity about the economic landscape.
Furthermore, economic events can influence consumer confidence, which in turn affects consumer spending. Businesses closely track economic indicators like the Consumer Confidence Index to gauge consumer sentiment and adjust their marketing and sales strategies accordingly.
5. Major Central Bank Announcements
5.1 Federal Reserve (Fed)
The Federal Reserve, often referred to as the Fed, is the central banking system of the United States. Its monetary policy decisions, including changes in interest rates and bond-buying programs, have a significant impact on the U.S. economy and global financial markets.
Traders and investors pay close attention to the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) meetings, where the Fed announces its decisions on interest rates and provides insights into its economic outlook and policy stance.
5.2 European Central Bank (ECB)
The European Central Bank is the central bank for the euro and oversees monetary policy for the Eurozone. Like the Fed, the ECB's decisions on interest rates and other policy measures can influence European and international financial markets.
The ECB's President holds press conferences after monetary policy meetings, providing explanations for their decisions and giving insights into the bank's economic assessment.
5.3 Bank of England (BoE)
The Bank of England is the central bank for the United Kingdom. Its monetary policy decisions impact the British economy and are closely watched by traders and investors globally.
The BoE releases policy statements and meeting minutes, which offer insights into the factors influencing their decisions on interest rates and asset purchases.
5.4 Bank of Japan (BoJ)
The Bank of Japan plays a crucial role in Japan's monetary policy and aims to maintain price stability and support economic growth.
Traders and investors analyze the BoJ's monetary policy statements and press conferences for indications of future policy changes that could affect the Japanese yen and Japanese asset prices.
6. Economic Data Releases
6.1 Non-Farm Payrolls (NFP)
The Non-Farm Payrolls report, released by the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, provides information on the number of jobs added or lost in the U.S. economy (excluding the farming sector).
This report is a key indicator of economic health and can influence the Federal Reserve's decisions on monetary policy.
6.2 Purchasing Managers' Index (PMI)
The PMI is an economic indicator that gauges the health of the manufacturing and services sectors. It is based on survey data from purchasing managers in various industries.
A PMI reading above 50 indicates economic expansion, while a reading below 50 suggests contraction.
6.3 Consumer Confidence Index
The Consumer Confidence Index measures consumers' optimism about the state of the economy and their personal financial situation.
High consumer confidence levels can lead to increased consumer spending, while low confidence levels may result in reduced spending and economic slowdown.
6.4 Housing Market Data
Housing market data includes information on home sales, housing starts, and home price indices.
The housing market is closely tied to consumer wealth and confidence, making this data crucial for understanding economic trends.
7. Geopolitical Events and Their Impact
7.1 Trade Wars and Tariffs
Geopolitical events such as trade wars and the imposition of tariffs can have far-reaching effects on the global economy and financial markets.
Trade tensions between countries can disrupt international trade flows, affect business operations, and lead to market volatility.
7.2 Political Elections and Outcomes
Political elections and their outcomes can significantly impact economic policies and market sentiment.
Investors closely watch elections for potential shifts in fiscal policies, regulations, and trade
relationships.
8. Natural Disasters and Economic Consequences
8.1 Hurricanes and Storms
Natural disasters like hurricanes and storms can cause widespread damage to infrastructure and disrupt economic activities in affected regions.
Rebuilding efforts after such events can stimulate economic growth in the long term.
8.2 Earthquakes and Tsunamis
Earthquakes and tsunamis can have devastating effects on communities and economies, leading to infrastructure damage and loss of productivity.
Recovery and reconstruction efforts are crucial for economic recovery.
9. Corporate Earnings Reports
9.1 Quarterly Earnings Calls
Publicly traded companies announce their quarterly earnings results through earnings calls and press releases.
Earnings reports influence stock prices and investor perceptions of a company's financial health.
9.2 Market Reaction to Earnings Reports
Positive earnings surprises can lead to stock price rallies, while negative earnings surprises can result in stock price declines.
Investors analyze earnings reports to make informed decisions about their investments.
10. Industry-Specific Events
10.1 Technology Conferences
Technology conferences and product launches can impact the stock prices of tech companies.
New product announcements and technological advancements can drive investor interest.
10.2 Automotive Shows
Automotive shows and product unveilings can influence the performance of automotive stocks.
Investors may respond to new vehicle models and technologies presented at these events.
11. Global Economic Summits
11.1 G7 and G20 Summits
The G7 and G20 Summits bring together leaders of major economies to discuss global economic issues.
Decisions made during these summits can have broad implications for financial markets.
11.2 World Economic Forum (WEF)
The World Economic Forum in Davos, Switzerland, attracts political and business leaders to discuss global economic challenges.
Market participants watch for any announcements or policy proposals arising from the event.
12. Black Swan Events
12.1 Definition and Examples
Black Swan events are rare and unexpected occurrences with severe consequences.
These events are challenging to predict and can lead to significant market disruptions.
12.2 Unpredictability and Economic Impact
The unpredictability of Black Swan events can cause panic and rapid market sell-offs.
Black Swan events can have lasting effects on the economy and financial markets.
13. Economic Calendar Tools
13.1 Online Economic Calendars
Online economic calendars offer real-time updates on economic events and data releases.
Traders and investors rely on these tools for timely information.
13.2 Mobile Apps for Economic Events
Mobile apps provide users with access to economic calendars on their smartphones and tablets.
These apps allow users to stay informed on the go.
14. Analyzing and Utilizing Economic Calendars
14.1 Traders and Investors
Traders and investors use economic calendars to plan their trading strategies.
They analyze economic data to make informed decisions about asset allocation.
14.2 Businesses and Corporations
Businesses and corporations use economic calendars to anticipate economic conditions.
This information guides business planning and risk management.
15. Economic Calendar and Personal Finance
15.1 Budgeting and Financial Planning
Individuals use economic calendars to plan their personal finances.
They may adjust spending and saving based on economic conditions.
15.2 Investment Strategies
Economic calendars help individuals plan their investment strategies.
Investors make choices based on economic events that may impact their portfolios.
16. The Future of Economic Calendars
16.1 Technological Advancements
Advancements in technology will enhance the accuracy and accessibility of economic calendars.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning may play a significant role in analyzing economic data.
16.2 Integration with AI and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning can assist in predicting market reactions to economic events.
These technologies may provide valuable insights for traders and investors.
17. Tips for Using Economic Calendars Effectively
17.1 Stay Updated and Organized
Regularly check economic calendars for updates on events and data releases.
Stay organized to track relevant information effectively.
17.2 Understand Data Sources
Be aware of the sources and reliability of economic data.
Different data providers may have varying methodologies.
18. Common Mistakes to Avoid with Economic Calendars
18.1 Overreaction to News
Avoid making hasty decisions based on immediate market reactions.
Consider long-term trends and underlying fundamentals.
18.2 Ignoring Geopolitical Events
Geopolitical events can have significant impacts on the economy.
Stay informed about geopolitical developments that may affect markets.
19. Case Studies of Market Reactions
19.1 Positive Economic Events
Explore examples of economic events that led to positive market reactions.
Understand the factors that contributed to the market's positive response.
19.2 Negative Economic Events
Study instances where economic events triggered negative market reactions.
Learn from these cases to prepare for potential downturns.
20. The Role of Media in Reporting Economic Events
20.1 Influence on Market Sentiment
Media reports can influence how investors perceive economic events.
Recognize the potential biases in media reporting.
20.2 Responsible Journalism
Responsible and accurate journalism is essential for providing reliable information to the public.
Be critical of sensationalized or misleading news reports.
21. Regulatory Changes and Economic Calendars
21.1 Impact on Financial Markets
Regulatory changes can have a significant impact on financial markets.
Be aware of upcoming regulatory announcements and their potential consequences.
21.2 Compliance and Transparency
Businesses must comply with changing regulations to avoid legal and financial risks.
Transparency in reporting is crucial for maintaining public trust.
22. Economic Calendar and International Trade
22.1 Trade Agreements and Tariffs
International trade agreements and tariffs can affect economic growth and market sentiment.
Monitor developments in trade negotiations and agreements.
22.2 Trade Balances and Deficits
Changes in trade balances can influence exchange rates and global trade dynamics.
Understand the implications of trade imbalances on the economy.
23. How Economic Calendars Shape Public Policy
23.1 Government Decision-Making
Government officials and policymakers rely on economic data to make informed decisions.
Economic calendars help shape public policies for economic stability and growth.
23.2 Economic Policies and Reforms
Economic calendars inform discussions about necessary policy changes and reforms.
Policymakers use economic data to assess the effectiveness of existing policies.
24. Understanding Market Volatility
24.1 Causes and Effects
Market volatility can result from various factors, including economic events and geopolitical developments.
Understand the root causes of market volatility.
24.2 Strategies to Navigate Volatile Markets
Investors can use different strategies to manage risks during volatile periods.
Diversification and risk management are essential components of such strategies.
25. Footnote
In conclusion, economic calendars are indispensable tools for anyone involved in financial markets, businesses, and policymaking. They provide vital information about key economic events, data releases, and announcements that can impact the economy and financial markets. Traders and investors use economic calendars to make informed decisions, while businesses rely on them for strategic planning. Staying updated with accurate economic data is crucial for success in today's dynamic global economy.
As technology advances, economic calendars are likely to become even more sophisticated, incorporating AI and machine learning to enhance their predictive capabilities. However, it is essential to exercise caution and avoid overreacting to immediate news and market fluctuations. Responsible journalism and transparent reporting play a crucial role in providing accurate information to the public.
Remember to check economic calendars regularly, understand the data sources, and consider geopolitical events when analyzing market trends. By doing so, individuals and businesses can navigate the complexities of the global economy and make sound financial decisions.











Discussion