Performance Analysis of the Top Ten Global Stock Indices in the Last Decade
Introduction
Over the past decade, the global stock market has experienced significant fluctuations, influenced by various economic, geopolitical, and technological factors. This article aims to provide a comprehensive performance analysis of the top ten global stock indices from the last decade, highlighting key trends, successes, and challenges faced by each index.
Table of Contents
- The Importance of Global Stock Indices
- Top Ten Global Stock Indices
- Factors Influencing Stock Index Performance
- Performance Analysis
- Major Contributors to Growth
- Challenges Faced by Global Stock Indices
- The Role of Central Banks
- Future Outlook
- Footnote
- FAQs
The Importance of Global Stock Indices
Global stock indices are critical indicators that represent the overall performance of the stock market in various regions around the world. These indices track the value of a specific group of stocks, offering investors insights into the broader economic trends and sentiment.
NASDAQ-100 - The High-Tech Giants Index
Average Volume: 5.7 Billion
Symbol: NDX
Country: USA
Weighting Method: Capitalization-Weighted
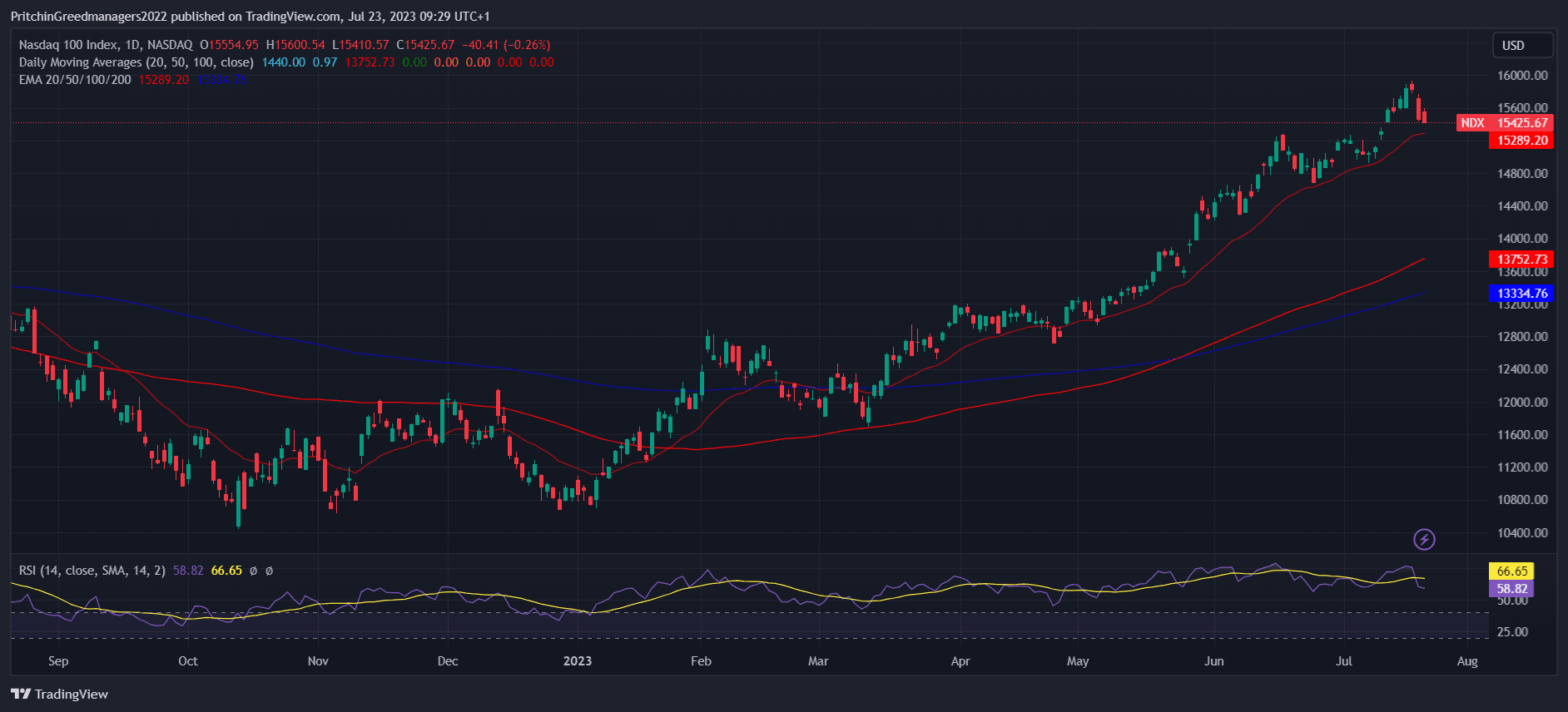
Image source from trading view
The NASDAQ-100, founded in 1985, is one of the largest US indices, comprising 103 shares of 100 high-tech US mid- and large-cap companies traded in the Nasdaq market system. This index predominantly features companies involved in Internet holdings, electronics, and software manufacturing.
The NASDAQ-100's exceptional growth is attributed to its focus on capitalization-weighted growth stocks. With a market cap of $9.8 trillion by the end of 2019, tech giants like Apple, Microsoft, Amazon, Facebook, Alphabet (Google), and Tesla significantly contribute to its impressive value.
S&P 500 - The Market Capitalization Leader
Average Volume: 5 Billion
Symbol: SPX
Country: USA
Weighting Method: Free-Float Capitalization-Weighted
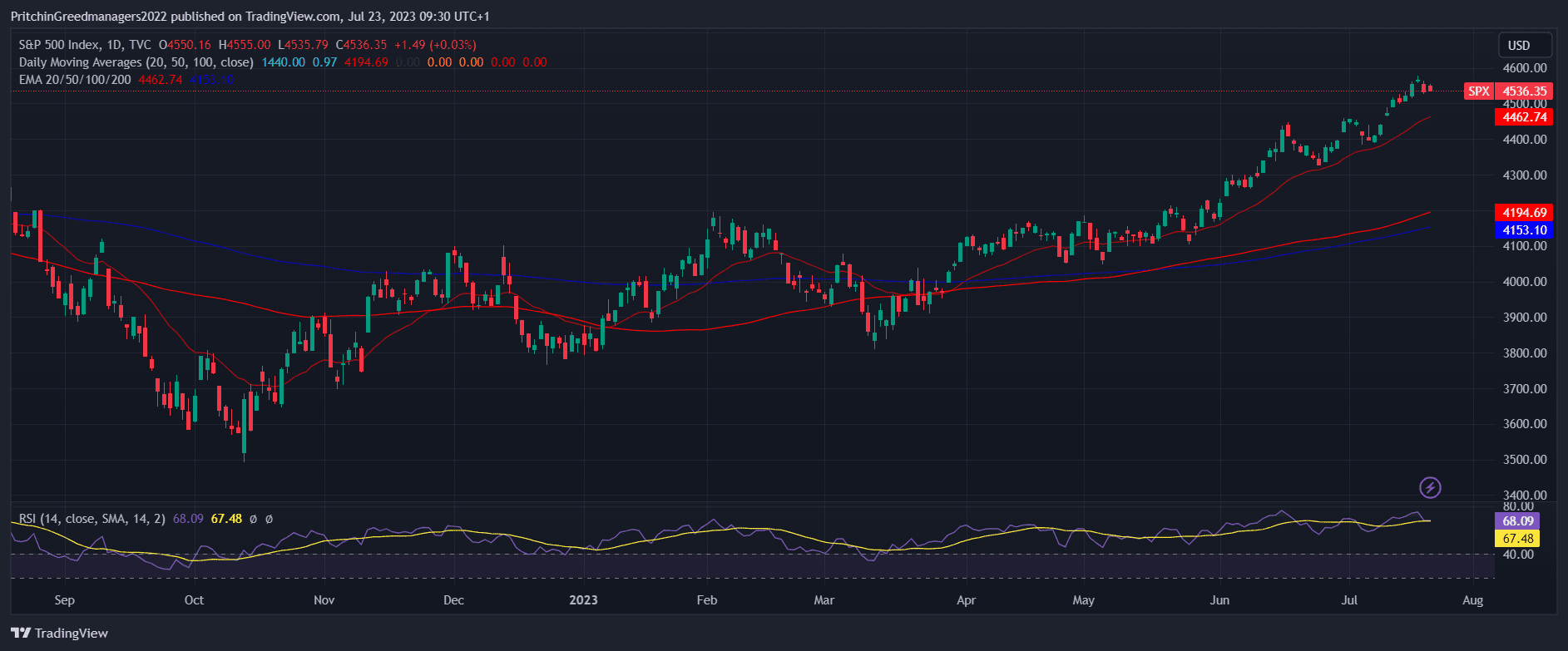
Image source from trading view
The Standard and Poor's Composite 500 Index, launched in 1957, is one of the main American stock indices, encompassing 505 shares of the 500 largest companies in the USA. These companies collectively account for around 80% of the entire US market's capitalization.
As one of the most influential stock indices globally, the S&P 500 holds the power to significantly impact the share indices of other countries. In December 2020, its market cap reached an astounding $33.4 trillion, with technology giants like Microsoft, Apple, Amazon, Facebook, Google, Berkshire Hathaway, Johnson&Johnson, and Visa dominating its composition.
Hang Seng Index - The Southeast Asian Powerhouse
Average Volume: 3 Billion
Symbol: HIS
Country: Hong Kong Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China
Weighting Method: Capitalization-Weighted
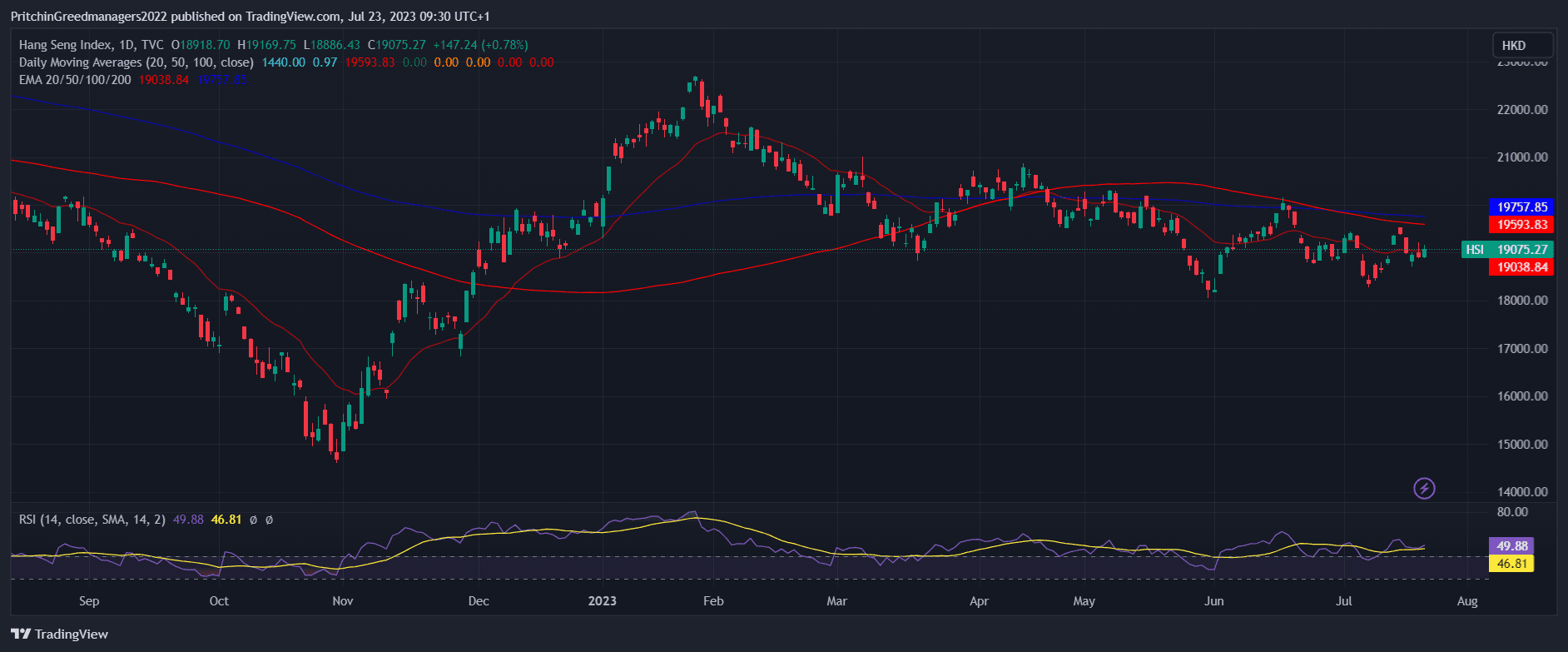
Image source from trading view
The Hang Seng Index, established in 1969, is the primary index of the Hong Kong Stock Exchange and a dominant force in Southeast Asia. This index represents approximately 65% of the total market cap of the Hong Kong Stock Exchange.
To facilitate easier calculations, the Hang Seng Index is divided into four sub-indices:
- Industrial Hang Seng Commerce & Industry
- Investment Hang Seng Properties
- Hang Seng Utilities, focusing on the energy sector
- Financial Hang Seng Finance
The index comprises massive corporations like HSBC, China Construction Bank, Industrial and Commercial Bank of China, and Bank of China, which are among the largest banks worldwide.
FTSE 100 - The British Giant
Average Volume: 900 Million
Symbol: FTSE
Country: UK
Weighting Method: Capitalization-Weighted

Image source from trading view
The Financial Times Stock Exchange 100 Index, initiated in 1984, is the major index of the UK. It consists of one hundred shares with the highest capitalization on the London Stock Exchange.
The FTSE 100, together with the Dow Jones Industrial Average, S&P 500, NASDAQ, and Nikkei 225 indices, forms the "big five indicators" of the global economy.
Encompassing companies operating in over 150 countries, the FTSE 100 boasted a market cap of £1.814 trillion as of May 2020. Notably, there are more than 200 indices worldwide with the same name "FTSE" and using the same calculation formula. Major players in this index include HSBC, Royal Dutch Shell, and BP.
Dow Jones Industrial Average - The Wall Street Legend
Average Volume: 400 Million
Symbol: DJI
Country: USA
Weighting Method: Price-Weighted
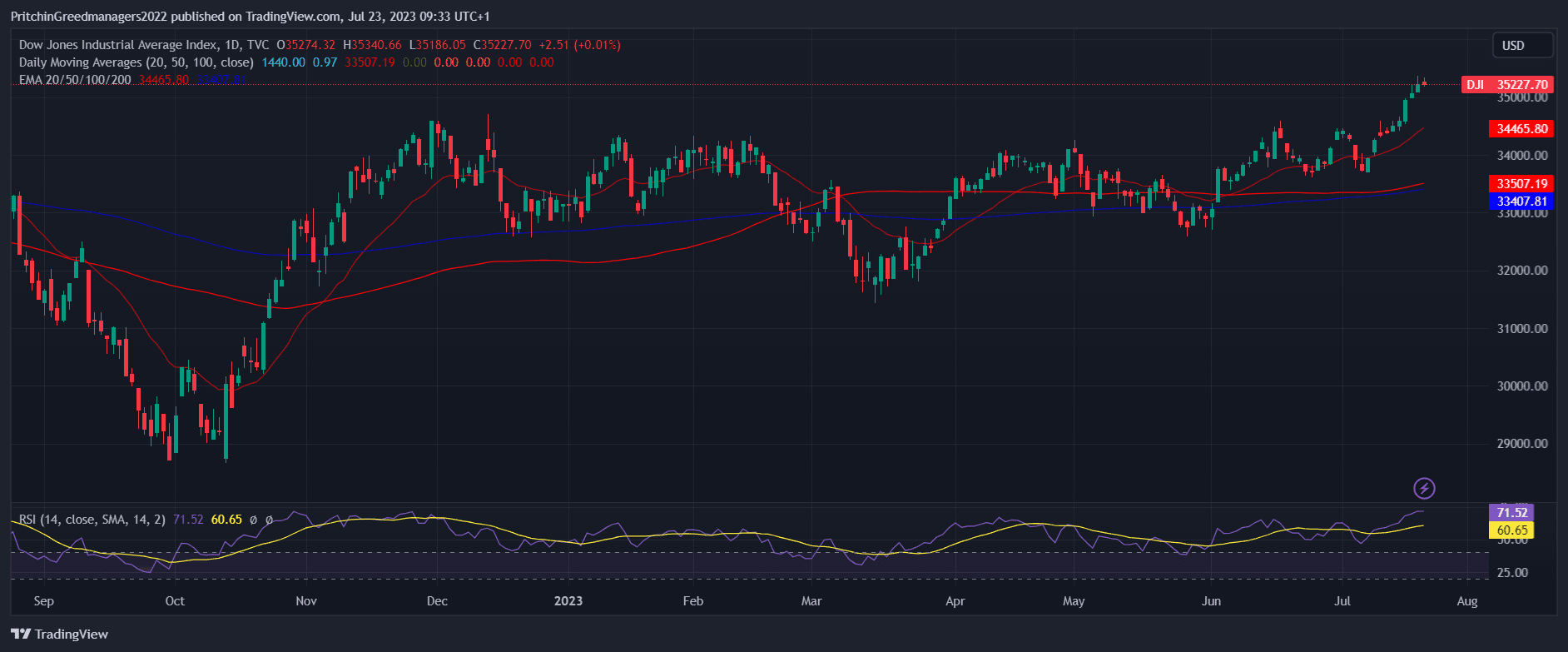
Image source from trading view
The Dow Jones Industrial Average, commonly known as the Dow, was first calculated in 1884 by Charles Dow, the publisher of The Wall Street Journal. Initially based on 11 railway companies, it was later expanded to include 30 large companies listed on US stock exchange markets, weighted by their prices.
The Dow Jones index is a crucial indicator of the US industrial sector and holds significant importance in the American economy. As of December 2019, its total market cap reached a staggering $8.33 trillion. Companies such as Coca-Cola, IBM, Intel, Microsoft, and General Motors are major constituents of this index.
DAX 30 - The German Powerhouse
Average Volume: 80 Million
Symbol: DAX
Country: Germany
Weighting Method: Capitalization-Weighted
Image source from trading view
Established in 1988, the DAX 30 is the primary German stock market index, comprising the 30 most liquid shares of the largest companies in Germany.
Similar to other global indices, the DAX serves as a barometer of its region's economy. Deutsche Börse AG calculates the index, which boasted a market cap of €1,017.7 billion as of September 2020.
Sub-indices based on the DAX 30 include CDAX, HDAX, MDAX, SDAX, TECDAX, and OKODAX, each focusing on specific segments of the market. Notable companies within the DAX 30 are BMW, Deutsche Bank, Allianz, Deutsche Post, Henkel, and others.
Russell 2000 - The Small-Cap Specialist
Average Volume: 50 Million
Symbol: RUT
Country: USA
Weighting Method: Free-Float Capitalization-Weighted
Image source from trading view
The Russell 2000 tracks the performance of small US companies and represents around 90% of the total number of small-cap companies in the American stock market.
Unlike "elite" indices like the S&P 500 and Dow Jones, the Russell 2000 offers a more in-depth analysis of the market, featuring companies that are less commonly known. Despite lower index returns, its broad diversification provides greater resistance to risk, making it an attractive investment opportunity. This index was first calculated in 1984.
CAC 40 - The French Powerhouses
Average Volume: 45 Million
Symbol: PX1
Country: France
Weighting Method: Capitalization-Weighted
Image source from trading view
The CAC 40, established in 1987, is the major index of the French stock market, consisting of 40 companies trading on Euronext Paris.
Unlike most world stock indices, the CAC 40 index experiences constant change as the list of companies is revised nearly every quarter. As of January 2020, the market cap of CAC 40 reached €1.832 trillion.
Leading companies within the CAC 40 operate in various sectors such as industrial goods and services, household goods, healthcare, and the oil and gas industry. Giants like L'Oreal, Renault, and Michelin are among its constituents.
Euro STOXX 50 - The Eurozone Leaders
Average Volume: 40 Million
Symbol: SX5E
Country: Eurozone
Weighting Method: Free-Float Market Capitalization-Weighted
Image source from trading view
The Euro STOXX 50 includes the 50 largest Eurozone companies from 19 economic sectors, with France and Germany dominating, accounting for nearly 70% of the index's market capitalization.
Calculated since February 1998, this index is denominated in five major EU currencies - Euro, US and Canadian dollars, British pound sterling, and Japanese yen.
In addition to the Euro STOXX 50, various sub-indices have emerged, like Euro Stoxx SubIndex Italy, France, Spain, and others, providing insights into the national economic strategies of these countries. Noteworthy companies within the Euro STOXX 50 include Deutsche Post, Deutsche Bank, AXA, BMW, Siemens, and Volkswagen Group.
Bovespa Index - Ibovespa - The Latin American Giant
Average Volume: 10 Million
Symbol: BVSP
Country: Brazil
Weighting Method: Free-Float Capitalization-Weighted
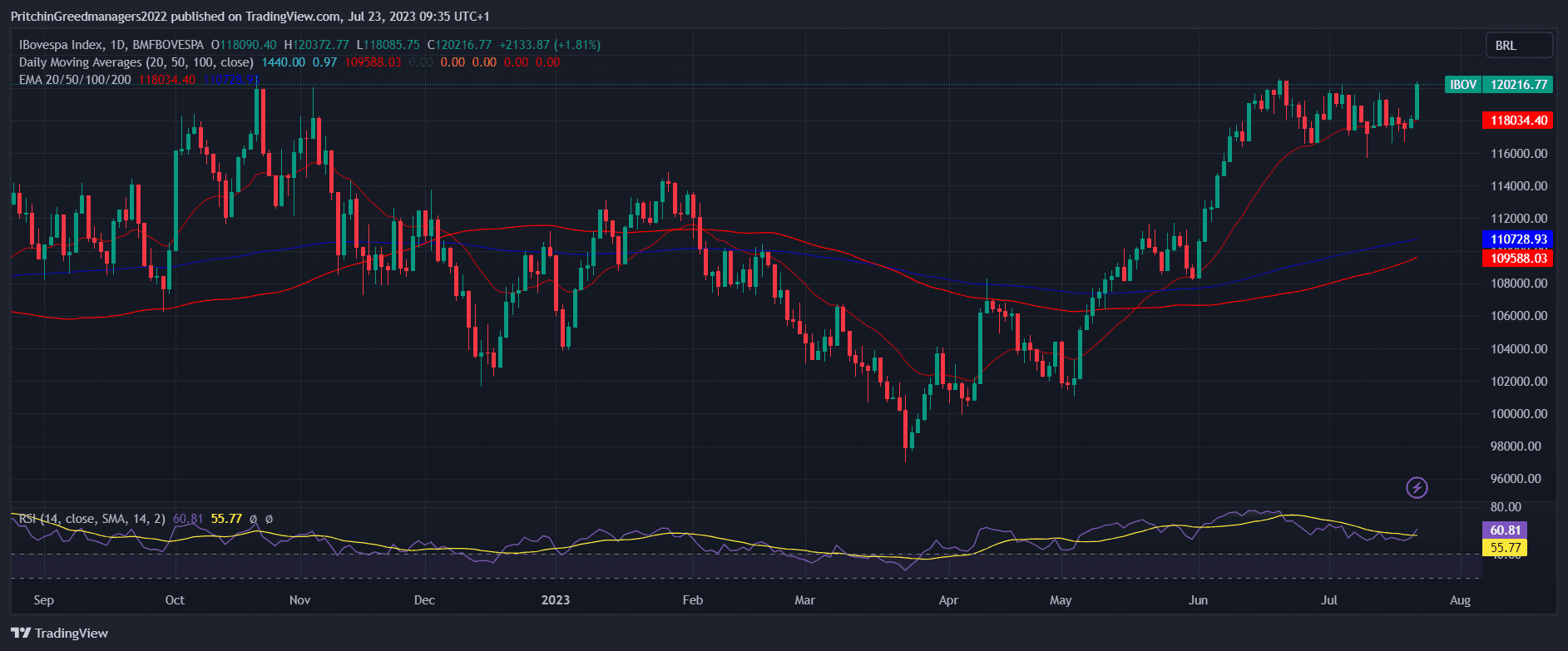
Image source from trading view
The Bovespa Stock Index, also known as Ibovespa, is a major macroeconomic indicator in Latin America, traded on the B3 stock exchange in Sao Paulo.
Comprising the "blue chips" of the 50 largest companies in Brazil, the Bovespa Index features three financial companies and eight energy sector representatives.
Ibovespa was first calculated in 1968 and includes sub-indices such as MLCX, SMLL, IEE, and INDX, focusing on specific aspects of the market. Prominent companies within the index include Petrobras, Itaú Unibanco, AmBev, Vale, and Telefônica Brasil.
Factors Influencing Stock Index Performance
The performance of stock indices is influenced by a wide range of factors that impact the overall market sentiment and economic conditions. Understanding these key factors is essential for investors to make informed decisions and navigate the complexities of the global stock market. Here are some of the primary factors that play a significant role in shaping the performance of stock indices:
- Economic Indicators- Economic indicators, such as GDP growth, employment rates, inflation, and consumer confidence, have a direct impact on the stock market. Positive economic indicators often lead to increased investor optimism, resulting in higher stock prices and overall index growth. On the other hand, weak economic data can lead to market downturns and lower index values.
- Geopolitical Events- Geopolitical events, such as trade wars, political instability, and international conflicts, can create uncertainty in the market. Traders and investors closely monitor geopolitical developments as they can significantly affect global trade, supply chains, and overall economic stability, thereby impacting stock indices.
- Technological Advancements- The influence of technology on stock indices has become increasingly prominent. Technological advancements and innovation can drive growth in specific sectors, such as the technology industry, and contribute to the overall performance of related indices.
- Natural Disasters- Natural disasters, such as earthquakes, hurricanes, and pandemics, can have both short-term and long-term effects on the stock market. These events can disrupt businesses, supply chains, and economies, leading to fluctuations in stock prices and index performance.
- Corporate Earnings and Financial Health- The financial performance of individual companies listed on an index plays a crucial role in determining the overall index performance. Positive earnings reports and strong financial health of companies within the index can lead to upward movements in the index value.
- Interest Rates and Monetary Policies- Central banks' decisions on interest rates and monetary policies can significantly impact the stock market. Lower interest rates can stimulate borrowing and investment, boosting stock prices, while higher rates may lead to lower market activity and index corrections.
- Investor Sentiment- Investor sentiment, often driven by emotions and perceptions, can heavily influence the stock market. Positive sentiment can result in a bullish market with rising index values, while negative sentiment can trigger bearish trends and declining indices.
- Market Liquidity- The liquidity of the market, which refers to the ease with which assets can be bought or sold, also affects stock index performance. Higher liquidity typically leads to more stable markets, while lower liquidity may result in increased volatility.
- Government Policies and Regulations- Government policies and regulations, particularly those related to taxation, trade, and industry-specific regulations, can impact the profitability of companies and industries represented in the stock indices.
- Global Economic Trends- Global economic trends, such as international trade dynamics and economic growth in different regions, can influence the performance of multinational companies and, consequently, global stock indices.
Performance Analysis
- Comparison of Returns- Over the last decade, several global stock indices have demonstrated remarkable returns, with the S&P 500, NASDAQ Composite, and Shanghai Composite leading the pack.
- Volatility and Risk Assessment- While high returns are enticing, investors also assess the level of volatility and risk associated with each index. Volatility can affect short-term gains, while long-term risk can impact overall investment strategies.
- Sector-Wise Analysis- Analyzing the performance of different sectors within each index can provide valuable insights into emerging trends and growth opportunities.
- Regional Performance- Regional economic developments and geopolitical events significantly impact the performance of stock indices in specific regions.
Major Contributors to Growth
- Technology Sector Boom- The surge in technology stocks, driven by innovation and digital transformation, has been a major contributor to the success of several global stock indices.
- Emerging Markets' Rise- The growth of emerging markets has captured investors' attention, leading to substantial returns in indices representing these regions.
- Stimulus Packages and Monetary Policies- Central banks' stimulus packages and accommodating monetary policies have injected liquidity into markets, boosting investor confidence and stock prices.
Challenges Faced by Global Stock Indices
Global stock indices encounter various challenges that can impact their performance and pose risks to investors. Understanding these challenges is crucial for market participants to develop resilient investment strategies. Below are some of the key challenges faced by global stock indices:
- Trade Wars and Tariffs- The escalation of trade tensions and the implementation of tariffs between countries can have a detrimental impact on stock markets worldwide. Trade disputes can disrupt global supply chains, affect international trade volumes, and create uncertainty, leading to market volatility and potential declines in stock index values.
- Global Economic Slowdown- Economic slowdowns, recessions, or periods of low growth in major economies can adversely affect stock indices. Reduced consumer spending, decreased business investments, and rising unemployment during economic downturns can lead to declining corporate earnings and negatively impact overall market sentiment.
- Geopolitical Instability- Geopolitical instability, including political unrest, civil conflicts, and international disputes, can create uncertainty in the global market. Investors become cautious during such times, leading to fluctuations in stock index values as they seek safe-haven assets.
- Natural Disasters and Climate Events- Natural disasters, such as earthquakes, hurricanes, floods, and wildfires, can cause significant damage to economies and businesses, resulting in disruptions to supply chains and production capabilities. Additionally, increasing concerns about climate change and its potential impacts on businesses have led to greater scrutiny and volatility in industries perceived to be environmentally sensitive.
- Global Health Crises- Pandemics and health crises, like the COVID-19 pandemic experienced in recent times, can have severe consequences for global stock indices. Such events can disrupt economic activities, lead to widespread lockdowns, and create uncertainties about the future, impacting investor confidence and stock market performance.
- Regulatory Changes- Changes in government regulations and policies can affect specific industries and companies represented in stock indices. Stricter regulations or unfavorable policy shifts can result in increased compliance costs and reduced profitability for affected companies.
- Technological Disruptions- Rapid technological advancements, while beneficial for some industries, can disrupt traditional business models and render certain companies and sectors obsolete. Investors need to be mindful of technological disruptions that can impact the performance of specific stock indices.
- Currency Fluctuations- For global stock indices with exposure to multiple currencies, fluctuations in exchange rates can influence the returns for foreign investors. Currency volatility can add complexity to investment decisions and introduce additional risks.
- Market Manipulation and Cybersecurity Threats- Instances of market manipulation, insider trading, and cybersecurity breaches can erode investor confidence and create market instability. Regulators and market participants continuously work to address these challenges and maintain market integrity.
- Black Swan Events- Black swan events, rare and unforeseen occurrences with severe consequences, can disrupt stock markets unexpectedly. These events, such as major terrorist attacks or unforeseen financial collapses, can have profound and lasting impacts on stock index performance.
The Role of Central Banks
Central banks play a critical role in influencing the performance and stability of stock indices through their monetary policies, regulatory measures, and actions to manage economic conditions. These institutions have significant power and responsibility in shaping the overall health of the financial markets and the broader economy. Here are some of the key roles central banks play in relation to stock indices:
- Monetary Policy- One of the primary functions of central banks is to formulate and implement monetary policy. Through this, they control the money supply, interest rates, and credit availability in the economy. By adjusting interest rates, central banks can influence borrowing costs for businesses and consumers. Lower interest rates can encourage borrowing and spending, leading to increased investments in the stock market, which can positively impact stock indices.
- Interest Rate Decisions- Central banks regularly review and set benchmark interest rates, such as the federal funds rate in the United States or the European Central Bank's main refinancing rate. Changes in interest rates can have a profound effect on investor behavior, affecting the attractiveness of different asset classes, including stocks. Lower interest rates can make equities more appealing to investors seeking higher returns, potentially boosting stock index performance.
- Quantitative Easing (QE)- In times of economic downturn or financial crisis, central banks may resort to quantitative easing. QE involves purchasing financial assets, such as government bonds or other securities, from the market to increase the money supply and inject liquidity into the economy. This can lead to lower long-term interest rates, increased investor confidence, and a potential rally in stock markets, positively affecting stock indices.
- Financial Stability and Regulation- Central banks are responsible for monitoring and maintaining financial stability. They oversee and regulate financial institutions to ensure their soundness and prevent systemic risks. A stable financial system can promote investor confidence and provide a favorable environment for stock market investments, benefiting stock indices.
- Currency Management- Central banks also manage the value of their national currency relative to other currencies. Currency interventions and foreign exchange policies can impact the competitiveness of domestic companies in international markets. A weaker domestic currency can boost export-oriented industries, positively influencing the performance of stock indices that include companies with significant foreign revenue exposure.
- Communication and Forward Guidance- Central banks communicate their policy decisions and economic outlook to the public, financial markets, and investors. The clarity of their forward guidance can shape market expectations and influence investor behavior. The tone and content of central bank statements can trigger market movements, potentially affecting stock indices.
- Crisis Management- During times of financial crises or economic shocks, central banks may take emergency measures to stabilize markets and prevent systemic risks. These measures can include providing liquidity support to financial institutions or implementing unconventional monetary policies. Such interventions can have an immediate impact on investor sentiment and stock index movements.
- Economic Forecasting- Central banks conduct economic forecasting and analysis to assess the overall health of the economy. Their projections and assessments can give valuable insights to investors and market participants, influencing their investment decisions and, subsequently, stock index performance.
Future Outlook
The future outlook of stock indices is a subject of great interest and speculation for investors, as it involves predicting the potential direction and performance of the stock market. While it is challenging to make precise forecasts, several factors and trends can provide insights into the possible trajectory of stock indices. Here are some key considerations for the future outlook of stock indices:
- Economic Recovery- The pace and strength of economic recovery from global crises, such as the COVID-19 pandemic, will significantly impact stock indices. As economies rebound, businesses recover, and consumer spending improves, stock markets may witness positive trends, potentially leading to higher index values.
- Technology and Innovation- Technological advancements and innovations continue to drive growth in various sectors, such as artificial intelligence, renewable energy, and biotechnology. Companies at the forefront of these industries could contribute to the growth of relevant stock indices, attracting investor interest.
- Market Regulation and Policies- Changes in government regulations and monetary policies can influence investor behavior and overall market sentiment. Investors closely monitor policy decisions made by central banks and governments as they can have profound effects on stock indices' performance.
- Global Trade and Geopolitical Relations- The resolution of trade tensions and improvements in geopolitical relations between major economies can create a favorable environment for stock markets. On the other hand, ongoing disputes and geopolitical uncertainties may introduce volatility and challenges for stock indices.
- Sustainability and ESG Investing- Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) considerations are gaining prominence in investment decision-making. Investors are increasingly focusing on companies that demonstrate sustainable practices and responsible corporate behavior, which may influence the performance of ESG-focused stock indices.
- Monetary Policy and Interest Rates- Central banks' decisions on interest rates and monetary policies will continue to impact investor sentiment and stock markets. Sudden changes in interest rates or unexpected shifts in policy direction can lead to market volatility and influence stock indices' movements.
- Technological Disruptions- As technology continues to evolve rapidly, disruptive innovations may reshape entire industries and pose challenges to traditional businesses. Investors will closely assess companies' adaptability to technological changes, potentially affecting stock indices.
- Emerging Markets Growth- The growth of emerging markets can have a significant impact on global stock indices. As these economies expand and become more integrated into the global market, companies from these regions may contribute to the performance of relevant stock indices.
- Public Health and Healthcare Sector- Developments in public health, advances in medical research, and the performance of the healthcare sector can influence stock indices. Companies involved in healthcare, pharmaceuticals, and biotechnology may experience growth or volatility, affecting relevant indices.
- Investor Sentiment and Speculation- Investor sentiment and speculative behavior can play a role in short-term movements of stock indices. Emotional responses to news and events can lead to market swings, but long-term fundamentals tend to drive sustainable growth in stock markets.
Footnote
The last decade witnessed remarkable growth and challenges for the top ten global stock indices. Economic developments, technological advancements, and geopolitical events have all played a significant role in shaping their performance. As we move into the future, investors will continue to closely monitor these indices, adapting their strategies to navigate the evolving landscape of the global stock market.
FAQs
1: How often are global stock indices updated?
- Global stock indices are typically updated in real-time as stock prices fluctuate during trading hours.
2: Which sector has contributed the most to the growth of these indices?
- The technology sector has been a major contributor to the growth of many global stock indices.
3: How do geopolitical events impact stock indices?
- Geopolitical events can create uncertainty and affect investor sentiment, leading to volatility in stock markets.
4: What are ESG considerations in investing?
- ESG stands for Environmental, Social, and Governance factors, which are increasingly considered by investors when making investment decisions.
5: How do investors manage risk in volatile markets?
- Investors manage risk by diversifying their portfolios, setting stop-loss orders, and conducting thorough research before making investment decisions.











Discussion