Forex trading strategies for using the Morning Star pattern: Techniques for trading with the Morning Star candlestick pattern.
In the fast-paced world of forex trading, where split-second decisions can make or break a trader's fortunes, having a comprehensive arsenal of strategies is essential. Candlestick patterns are a popular tool in a trader's toolkit, offering valuable insights into potential market reversals and trend shifts. One such pattern that has gained recognition for its reliability is the Morning Star pattern. In this article, we'll delve into the techniques for trading with the Morning Star candlestick pattern, exploring its significance, characteristics, and effective strategies.
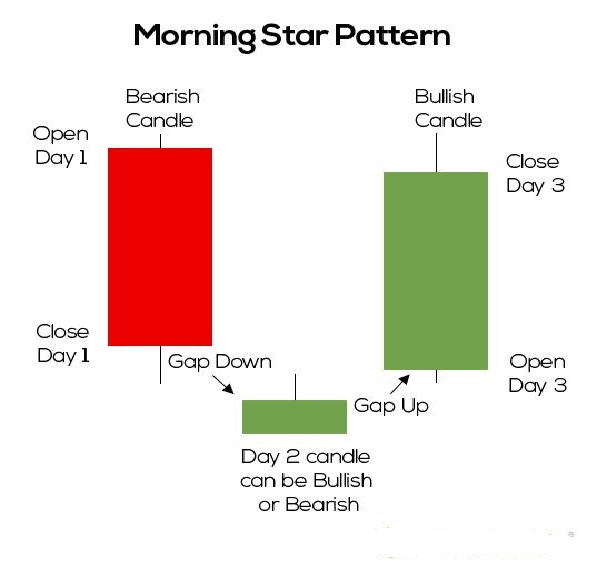
Table Content
I. Understanding the Morning Star Pattern
II. Characteristics of the Morning Star Pattern
1. First Candle
2. Second Candle
3. Third Candle
III. Techniques for Trading with the Morning Star Pattern
1. Confirmation through Volume Analysis
2. Waiting for Confirmation
3. Utilizing Additional Indicators
4. Applying Risk Management
5. Timeframe Considerations
6. Back-testing and Practice
IV. Real-Life Example: Trading with the Morning Star Pattern
1. Identifying the Pattern
2. Confirmation
3. Volume Analysis
4. Additional Indicators
5. Entry and Stop-Loss
6. Target
7. Risk Management
8. Monitoring and Adjustment
V. Footnote
Understanding the Morning Star Pattern
The Morning Star is a bullish reversal pattern found on candlestick charts. It consists of a series of three candles that collectively signal a potential shift from a downtrend to an uptrend. This pattern often appears at the end of a downtrend, indicating that a period of selling pressure might be coming to an end and buyers could regain control of the market. The Morning Star pattern is considered a strong indication of a trend reversal, but like any trading signal, it's crucial to confirm it with other technical and fundamental analysis.
Characteristics of the Morning Star Pattern
To effectively trade using the Morning Star pattern, traders need to identify its key characteristics:
1. First Candle: The pattern begins with a bearish (downward) candlestick, which signifies the continuation of the existing downtrend.
2. Second Candle: The second candle is a small-bodied candle that might be bullish or bearish. Its role is to indicate indecision in the market.
3. Third Candle: The third candle is a strong bullish (upward) candle that closes well beyond the midpoint of the first candle. This signifies a potential reversal and the emergence of buying pressure.
Techniques for Trading with the Morning Star Pattern
1. Confirmation through Volume Analysis
While the Morning Star pattern itself holds significance, confirming its reliability through volume analysis enhances its effectiveness. An increase in trading volume during the appearance of the Morning Star pattern strengthens the likelihood of a trend reversal. Higher volume suggests that more traders are participating in the new trend direction, validating the pattern's potential.
2. Waiting for Confirmation
As with any trading signal, it's advisable to wait for confirmation before taking action. In the case of the Morning Star pattern, traders often wait for a subsequent candle to close above the high of the third candle. This confirms that the bullish momentum is indeed taking hold, reducing the risk of false signals.
3. Utilizing Additional Indicators
To increase the accuracy of trading decisions based on the Morning Star pattern, traders can combine it with other technical indicators. Moving averages, relative strength index (RSI), and trendlines can provide supplementary information that strengthens the trading signal's reliability.
4. Applying Risk Management
Effective risk management is paramount in forex trading. Traders should never disregard the importance of setting stop-loss orders to limit potential losses. When trading based on the Morning Star pattern, placing a stop-loss below the low of the pattern's third candle can safeguard against unexpected reversals.
5. Timeframe Considerations
The timeframe a trader selects plays a crucial role in the effectiveness of trading strategies. When using the Morning Star pattern, it's advisable to consider higher timeframes, such as the daily or weekly charts. Higher timeframes offer more reliable signals, as they filter out some of the noise present in lower timeframes.
6. Back-testing and Practice
As with any trading strategy, practice makes perfect. Traders are encouraged to backtest the Morning Star pattern on historical data to assess its effectiveness in various market conditions. This practice not only hones trading skills but also helps traders understand the pattern's strengths and limitations.
Real-Life Example: Trading with the Morning Star Pattern
Let's illustrate the application of the Morning Star pattern with a hypothetical forex trading scenario:
1. Identifying the Pattern: On the daily chart of a currency pair, you notice a Morning Star pattern forming at the end of a downtrend. The first candle is a bearish candle, followed by a small-bodied candle indicating indecision. The third candle is a strong bullish candle that closes well above the midpoint of the first candle.
2. Confirmation: You decide to wait for confirmation. The next day, the price continues to rise, and the candle closes above the high of the third candle in the pattern.
3. Volume Analysis: You observe that the trading volume during the formation of the Morning Star pattern was significantly higher than the average trading volume of the past few days, indicating strong market participation.
4. Additional Indicators: You check the RSI and notice that it has moved out of the oversold territory, supporting the idea of a potential trend reversal.
5. Entry and Stop-Loss: With the confirmation in place, you enter a long position on the currency pair, placing a stop-loss just below the low of the third candle in the Morning Star pattern.
6. Target: You set a profit target based on a key resistance level identified through technical analysis.
7. Risk Management: Considering your overall risk tolerance, you ensure that the position size and stop-loss placement align with your risk management strategy.
8. Monitoring and Adjustment: As the trade progresses, you continue to monitor the price movement. If the price approaches your profit target, you might consider trailing your stop-loss to secure potential profits.
Footnote:
The Morning Star pattern is a powerful tool in a forex trader's toolkit, offering a reliable indication of potential trend reversals. However, it's important to remember that no trading strategy is foolproof. Successful trading involves a combination of technical analysis, fundamental understanding, risk management, and psychological discipline.
Traders who master the art of identifying and trading with the Morning Star pattern, while also considering confirmation signals and supplementary indicators, stand a better chance of making informed and profitable trading decisions. As with any trading strategy, continuous learning, practice, and adaptation to evolving market conditions are essential for achieving sustainable success in the dynamic world of forex trading.











Discussion