Forex Trading Strategies for Professionals: Advanced Approaches for Seasoned Forex Traders
Welcome to the world of advanced Forex trading strategies, where seasoned traders take their skills to the next level. In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into the techniques and approaches that professionals use to navigate the complex and dynamic forex market successfully.
Table of Contents
1. The Importance of Advanced Strategies
2. Fundamental Analysis: A Cornerstone
3. Technical Analysis Techniques
4. Advanced Chart Patterns
5. Mastering Advanced Indicators
6. Risk Management Strategies
7. Developing a Robust Trading Plan
8. Advanced Order Types
9. High-Frequency Trading
10. Algorithmic Trading
11. Psychology of Advanced Traders
12. Cryptocurrency Trading Strategies
13. Global Economic Factors
14. Advanced Hedging Techniques
15. Building a Forex Trading Network
16. Case Studies: Real-Life Examples
17. Understanding Regulatory Changes
18. Keeping Up with Technological Advancements
19. Maintaining Work-Life Balance
20. Continuous Learning and Education
21. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
22. Footnote
The Importance of Advanced Strategies
As seasoned forex traders, understanding the significance of advanced trading strategies is paramount. These techniques go beyond the basics, enabling professionals to navigate the complexities of the forex market more effectively. These strategies allow traders to adapt to changing market conditions, minimize risks, and capitalize on opportunities that may elude novice traders.
Fundamental Analysis: A Cornerstone
Fundamental analysis remains a cornerstone for professionals. Evaluating economic indicators, geopolitical events, and central bank policies helps traders make informed decisions. Proficient traders consider factors such as GDP growth, inflation rates, and employment data to anticipate currency movements.
Technical Analysis Techniques
a. Moving Averages
Moving averages smooth out price data to identify trends. Traders often use combinations of short-term and long-term moving averages to spot potential entry and exit points.
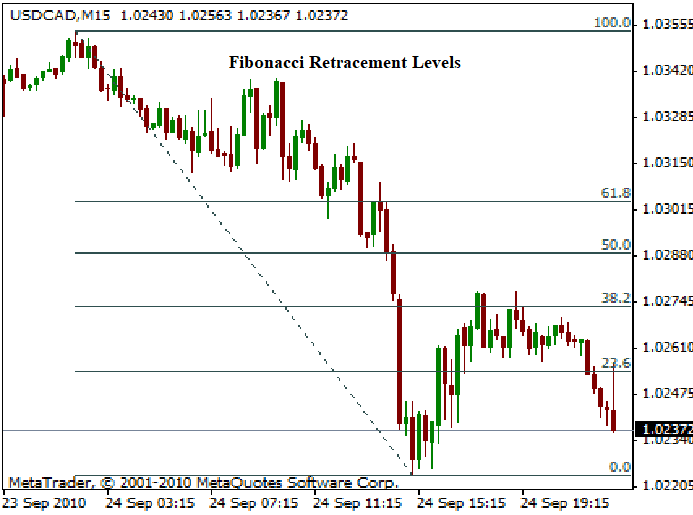
b. Fibonacci Retracements
Fibonacci retracements help traders identify potential support and resistance levels based on the Fibonacci sequence. These levels assist in predicting price reversals.
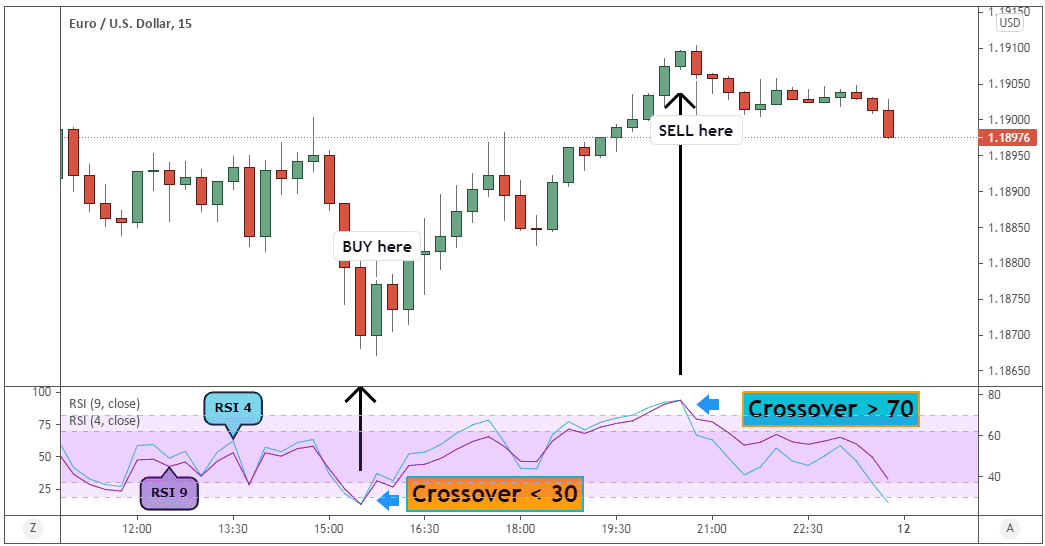
c. Relative Strength Index (RSI)
RSI measures the magnitude of recent price changes to evaluate overbought or oversold conditions. It's a valuable tool to identify potential trend reversals.
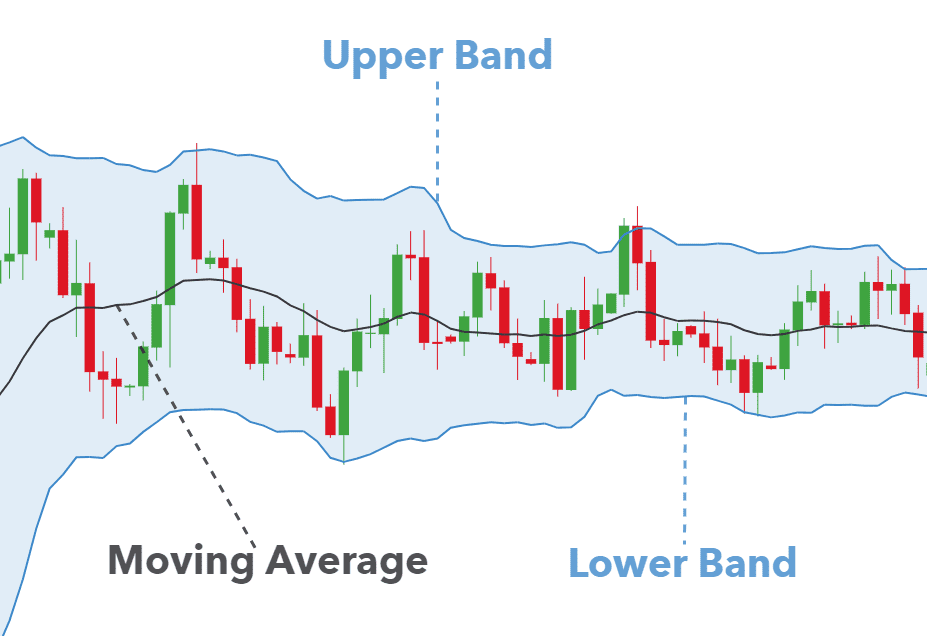
d. Bollinger Bands
Bollinger Bands encompass price movements by calculating volatility levels. Traders use them to identify periods of high or low volatility and potential price breakouts.
Advanced Chart Patterns
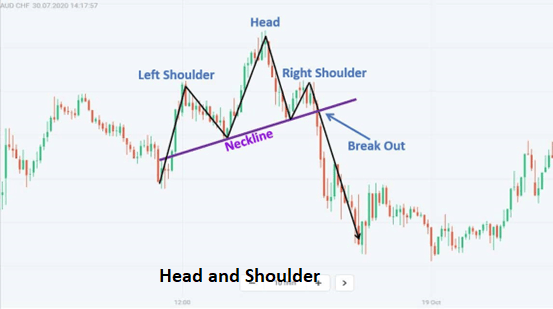
i) Head and Shoulders
The head and shoulders pattern is a reversal pattern indicating a potential trend change. It consists of three peaks—a higher peak (head) between two lower peaks (shoulders).
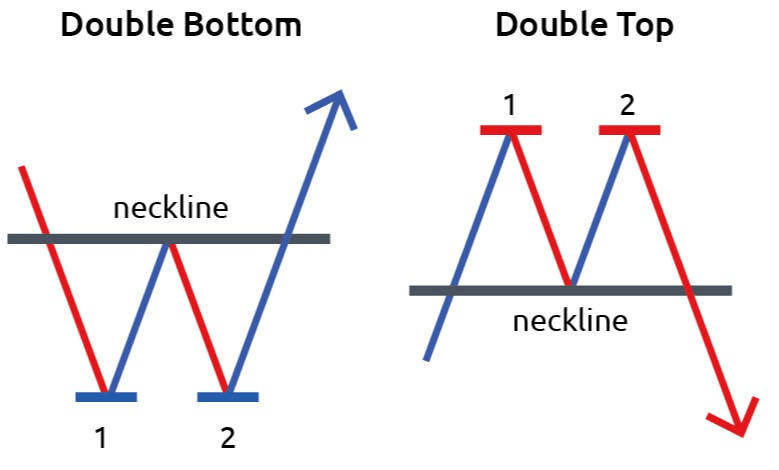
ii) Double and Triple Tops/Bottoms
These patterns occur when prices hit a resistance (top) or support (bottom) level twice or thrice, signaling potential trend reversals.
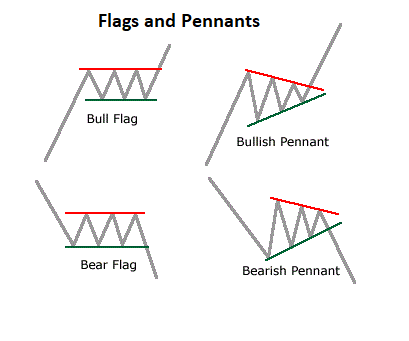
iii) Flags and Pennants
Flags and pennants are continuation patterns. Flags are rectangular-shaped, while pennants resemble small symmetrical triangles. They indicate short-term consolidation before the previous trend resumes.
Mastering Advanced Indicators
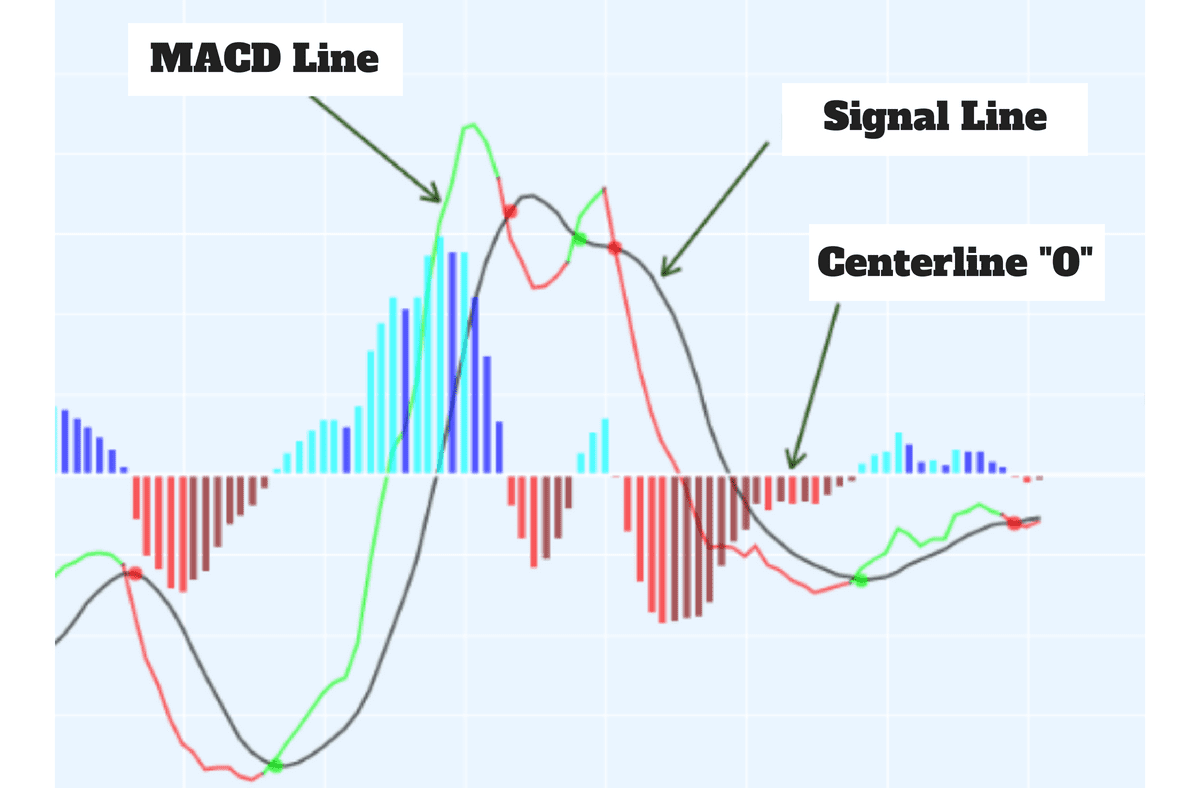
A) MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence)
MACD combines moving averages to reveal potential trend changes and momentum shifts. It consists of a MACD line, signal line, and histogram.
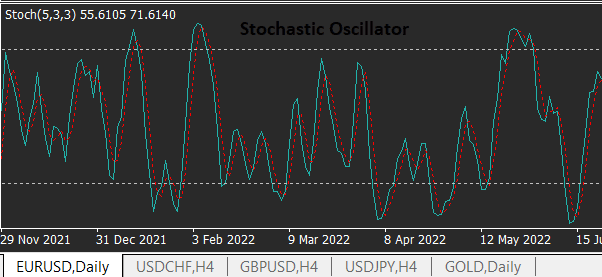
B) Stochastic Oscillator
The stochastic oscillator identifies overbought and oversold conditions. It consists of two lines (%K and %D) that fluctuate between 0 and 100.
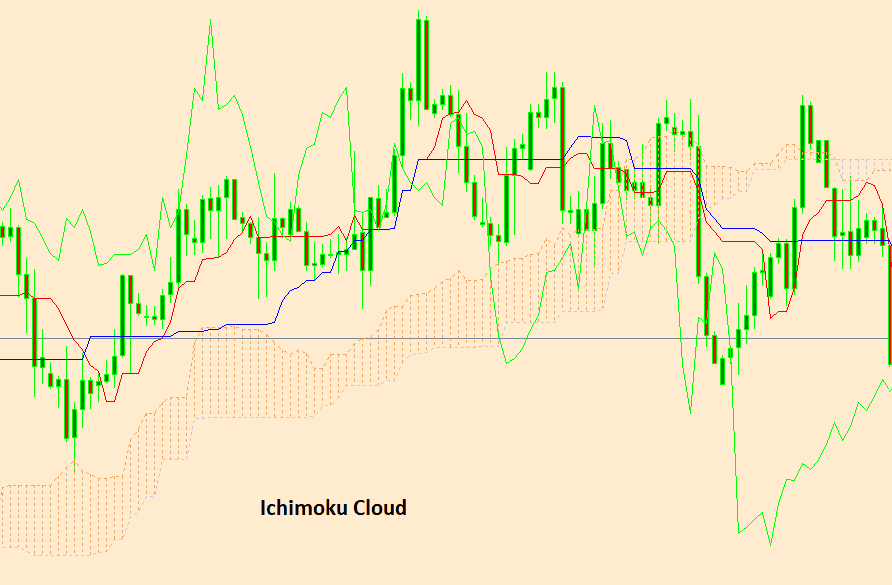
C) Ichimoku Cloud
Ichimoku Cloud is a comprehensive indicator providing insights into support, resistance, and trend direction. It includes several components like the Tenkan-sen, Kijun-sen, and Senkou Span lines.
Risk Management Strategies
a) Position Sizing
Determining the appropriate position size relative to account balance and risk tolerance is crucial. Professionals adhere to position sizing rules to limit potential losses.
b) Diversification
Seasoned traders diversify their portfolios to spread risk across various currencies and assets, reducing the impact of a single loss.
c) Setting Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Levels
Setting stop-loss and take-profit levels ensures traders exit positions at predefined points, preventing substantial losses and securing profits.
Developing a Robust Trading Plan
i) Goal Setting
Establishing clear trading goals helps professionals stay focused and disciplined. Goals can encompass profit targets, risk limits, and performance benchmarks.
ii) Strategy Selection
Choosing appropriate strategies based on market conditions and personal strengths is essential. Different strategies suit varying degrees of market volatility.
iii) Backtesting and Optimization
Professionals rigorously test strategies on historical data to assess their viability. Optimization involves refining strategies to maximize their effectiveness.
Advanced Order Types
i) Limit and Stop-Limit Orders
Limit orders specify a maximum price to buy or minimum price to sell. Stop-limit orders combine stop and limit orders to trigger trades at specific price levels.
ii) Trailing Stops
Trailing stops automatically adjust as prices move in favor of the trade. They lock in profits while allowing room for price fluctuations.
iii) OCO (One-Cancels-the-Other) Orders
OCO orders link two orders together, where executing one automatically cancels the other. It's useful for placing both stop-loss and take-profit orders simultaneously.
High-Frequency Trading
a) Strategies and Considerations
High-frequency trading involves executing a large number of orders in milliseconds. Strategies often revolve around exploiting small price differentials.
b) Risks and Benefits
While high-frequency trading offers potential for quick profits, it comes with risks like technology failures and market manipulation concerns.
Algorithmic Trading
i) Building and Testing Algorithms
Algorithmic trading relies on pre-programmed instructions to execute trades. Traders develop, backtest, and fine-tune algorithms for optimal performance.
ii) Monitoring and Adjusting
Continuous monitoring ensures algorithms perform as intended. Traders must be ready to adjust algorithms to adapt to evolving market conditions.
Psychology of Advanced Traders
a) Emotion Management
Maintaining emotional discipline is crucial. Advanced traders learn to control emotions like fear and greed to make rational decisions.
b) Patience and Discipline
Professionals understand the significance of patience and discipline in waiting for high-probability trading setups.
Cryptocurrency Trading Strategies
i) Unique Aspects of Crypto Markets
Crypto markets operate 24/7, and their volatility provides unique opportunities and risks. Traders adapt strategies to account for these differences.
ii) HODLing vs. Active Trading
Traders decide between long-term holding (HODLing) and active trading based on their risk appetite and market outlook.
Global Economic Factors
i) Impact of Economic Indicators
Global economic events influence currency movements. Traders track indicators like interest rates, unemployment rates, and inflation data.
ii) Geopolitical Events
Geopolitical developments, such as trade agreements and conflicts, can trigger significant currency fluctuations.
Advanced Hedging Techniques
i) Currency and Interest Rate Swaps
Professionals use currency swaps to hedge against currency risk in international transactions. Interest rate swaps manage interest rate risk.
ii) Options and Derivatives
Options and derivatives provide flexible hedging strategies, allowing traders to mitigate risk exposure.
Building a Forex Trading Network
A) Mentorship and Collaboration
Connecting with experienced traders offers insights and guidance. Collaborating with peers fosters knowledge exchange.
B) Staying Informed and Networking
Professionals actively participate in industry events, forums, and online communities to stay updated and exchange ideas.
Case Studies: Real-Life Examples
i) Successful Trades and Strategies
Examining past successful trades provides valuable learning opportunities and insights into effective strategies.
ii) Learning from Mistakes
Analyzing unsuccessful trades helps professionals identify pitfalls and refine their approaches.
Understanding Regulatory Changes
a) Adapting to New Rules and Laws
Global forex markets are subject to regulatory changes. Adapting to new rules ensures compliance and prevents legal issues.
b) Navigating Taxation and Reporting
Professionals must understand tax implications and reporting requirements for forex trading profits.
Keeping Up with Technological Advancements
i) AI and Machine Learning in Trading
Artificial intelligence and machine learning aid in data analysis, pattern recognition, and predictive modeling.
ii) Automation and Algorithmic Advances
Advancements in automation enable traders to execute trades efficiently based on pre-set conditions.
Maintaining Work-Life Balance
i) Avoiding Burnout
Balancing trading with personal life prevents burnout. Taking breaks and engaging in hobbies are essential.
ii) Time Management
Efficient time management ensures traders allocate time to research, trade execution, and personal pursuits.
Continuous Learning and Education
a) Seminars and Webinars
Attending seminars and webinars exposes professionals to new ideas, strategies, and industry trends.
b) Industry Literature and Research
Reading books, research papers, and industry reports helps traders stay updated on emerging market trends.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is the significance of advanced forex strategies for professionals?
A: Advanced strategies help professionals navigate market complexities and seize opportunities effectively.
Q: How does fundamental analysis impact forex trading?
A: Fundamental analysis involves evaluating economic indicators, influencing trading decisions based on global events.
Q: What are the key technical indicators for advanced traders?
A: Technical indicators like MACD, RSI, and Bollinger Bands assist in predicting price movements and trends.
Q: How do professionals manage risk in forex trading?
A: Risk management techniques include position sizing, diversification, and setting stop-loss and take-profit levels.
Q: What is the role of algorithmic trading in advanced forex strategies?
A: Algorithmic trading involves using pre-programmed instructions to execute trades based on specific criteria.
Q: How can traders maintain emotional discipline?
A: Managing emotions like fear and greed helps traders make rational decisions and avoid impulsive actions.
Q: What are the unique aspects of cryptocurrency trading?
A: Cryptocurrency markets operate 24/7 and are highly volatile, offering distinct opportunities and challenges.
Q: How do professionals stay informed about global economic factors?
A: Tracking economic indicators and geopolitical events helps traders anticipate currency movements.
Q: What are some advanced hedging techniques used by professionals?
A: Currency swaps, interest rate swaps, options, and derivatives are common hedging strategies.
Q: How can traders strike a balance between trading and personal life?
A: Balancing work and personal life through efficient time management and self-care practices is essential.
Footnote
Mastering advanced forex trading strategies requires dedication, continuous learning, and disciplined execution. By combining fundamental and technical analysis, risk management, and innovative approaches, professionals can navigate the dynamic forex market with confidence. Embracing evolving technologies and staying informed about global economic factors contribute to sustained success in the world of forex trading.











Discussion