Forex trading strategies for hedging: Approaches for using hedging to reduce potential losses.
The foreign exchange (forex) market is known for its dynamic and volatile nature. Traders engage in forex trading to capitalize on price fluctuations and make profits. However, with high volatility comes increased risk. To mitigate potential losses, traders often turn to hedging strategies. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of forex trading strategies for hedging and explore various approaches to effectively manage risk.
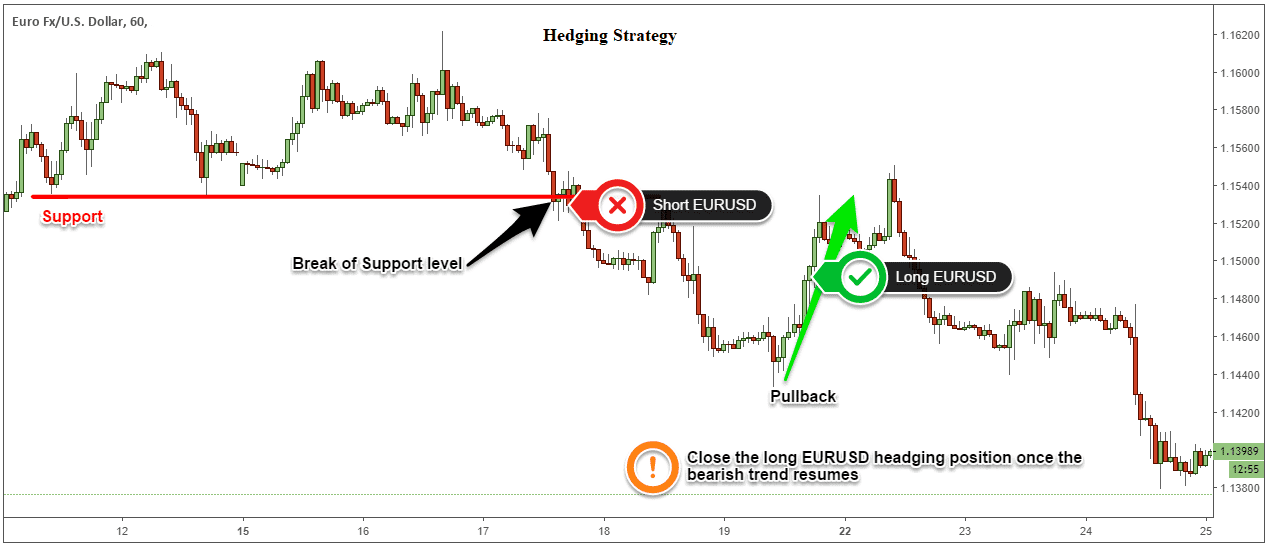
Table of Contents
- Understanding Forex Hedging
- Common Forex Hedging Strategies
- Implementing Forex Hedging Strategies
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Forex Hedging
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Footnote
1. Understanding Forex Hedging
Forex hedging is a risk management strategy used by traders and investors to protect themselves from potential losses due to unfavorable price movements in the currency market. Hedging involves opening positions that offset potential losses in another trade, thereby reducing overall risk exposure.
2. Common Forex Hedging Strategies
Simple Forex Hedging
Simple forex hedging involves opening a second position that is opposite to an existing trade. For instance, if a trader holds a long position (buy) on a currency pair, they would open a short position (sell) on the same pair. This way, if the market moves against their original position, the second trade helps mitigate losses.
Multiple Currency Pairs Hedging
This strategy involves trading correlated currency pairs simultaneously. If a trader holds a long position on one currency pair, they can open a short position on another pair that tends to move in the opposite direction. This way, losses in one position can be offset by gains in the other.
Options-Based Hedging
Options provide traders with the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a currency pair at a predetermined price within a specific time frame. Traders can use options to protect their positions from adverse market movements. For example, purchasing a put option can help limit potential losses in a long position.
Forward Contracts
Forward contracts are agreements to buy or sell a currency pair at a predetermined price on a future date. Traders can use forward contracts to lock in exchange rates and protect themselves from future volatility. This is particularly useful for businesses engaged in international trade.
Money Market Hedge
The money market hedge involves using the money market (short-term lending and borrowing) to offset potential losses. Traders can borrow or lend funds in a different currency to balance out potential losses in their forex positions.
Implementing Forex Hedging Strategies
Risk Assessment
Before implementing any hedging strategy, traders must conduct a thorough risk assessment. This involves analyzing the potential impact of market movements on their existing positions and identifying the most significant sources of risk.
Selecting the Right Strategy
The choice of hedging strategy depends on the trader's risk tolerance, market outlook, and trading goals. Each strategy has its own advantages and limitations, so it's crucial to select the one that aligns with the trader's overall approach.
Integration with Trading Plan
Hedging strategies should be an integral part of a trader's overall trading plan. The plan should outline when and how to use hedging, as well as the criteria for exiting hedged positions. Consistency and discipline are key to successful implementation.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Forex Hedging
Advantages:
- Risk Reduction: The primary benefit of forex hedging is its ability to minimize potential losses during unfavorable market conditions.
- Increased Flexibility: Traders have the flexibility to choose from various hedging strategies based on their preferences and market outlook.
- Portfolio Protection: Hedging can help protect an entire portfolio from currency-related risks, especially for international investors.
Disadvantages:
- Costs: Some hedging strategies, such as options and forward contracts, come with associated costs, which can eat into potential profits.
- Complexity: Certain hedging strategies, like options-based hedging, can be complex and require a good understanding of options markets.
- Reduced Profit Potential: While hedging reduces potential losses, it can also limit potential gains if the market moves favorably.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Is forex hedging suitable for all traders?
A: Forex hedging is suitable for traders who prioritize risk management. It might not be ideal for aggressive traders seeking high returns.
Q2: How do I choose the right currency pairs for multiple currency pairs hedging?
A: Choose currency pairs that have a strong historical correlation but tend to move in opposite directions. For instance, EUR/USD and USD/CHF often exhibit such behavior.
Q3: Can individual retail traders access forward contracts?
A: Forward contracts are commonly used by institutions and businesses for commercial purposes. Retail traders might find it challenging to access them.
Q4: Are there any hedging strategies that don't involve additional costs?
A: Simple forex hedging, where you open an opposite position, usually doesn't involve additional costs apart from spreads and potential overnight fees.
Footnote
Forex trading strategies for hedging play a crucial role in managing risk and protecting traders' capital from adverse market movements. By understanding the various hedging approaches available and integrating them into a well-defined trading plan, traders can navigate the dynamic forex market with more confidence and resilience. Remember that while hedging can mitigate losses, it's important to strike a balance between risk reduction and profit potential. As with any trading strategy, continuous learning, practice, and adaptation are key to achieving success in the forex market.











Discussion