Forex Trading Strategies for Carry Pairs in Range-Bound Markets: Techniques for the Carry Trade Strategy in Sideways Markets
The foreign exchange (forex) market is renowned for its volatility and the opportunities it offers to traders. Among the many trading strategies available, one that has gained popularity over the years is the carry trade strategy. This strategy involves taking advantage of interest rate differentials between two currencies by buying a currency with a higher interest rate while selling a currency with a lower interest rate. The aim is to profit from the interest rate differential, also known as the "carry."
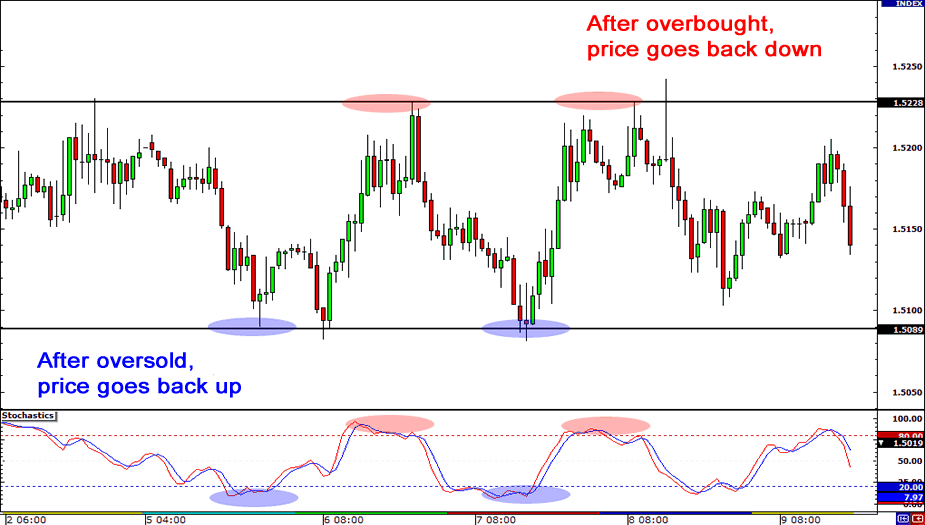
However, the forex market isn't always trending in one direction. In fact, there are periods when currency pairs move within a defined range, known as range-bound or sideways markets. During these times, the traditional carry trade strategy may not be as effective, as the lack of clear trend direction can limit the potential gains. In this article, we'll explore techniques for adapting the carry trade strategy to range-bound markets, maximizing its effectiveness even when the market lacks a clear trend.
Table Content
1. Understanding the Carry Trade Strategy
2. Challenges in Range-Bound Markets
3. Adapting the Carry Trade for Range-Bound Markets
4. Risk Management in Range-Bound Carry Trades
5. Footnote
Understanding the Carry Trade Strategy
Before delving into adapting the carry trade strategy for range-bound markets, let's briefly recap the basics of the strategy itself. The carry trade involves borrowing funds in a currency with a low-interest rate and using those funds to invest in a currency with a higher interest rate. The trader aims to profit from the difference between the interest rates, known as the "carry."
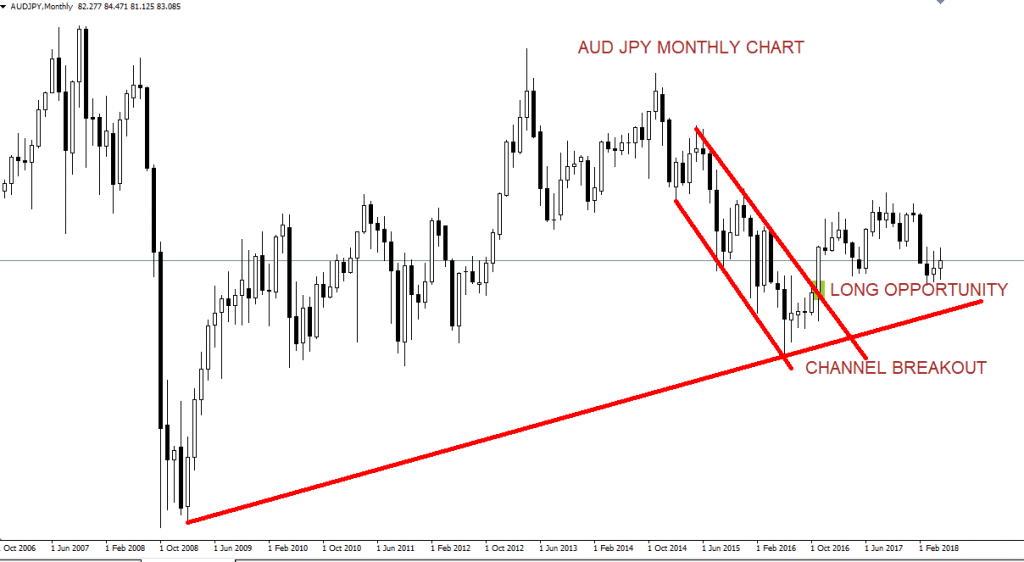
For instance, consider a trader who borrows funds in a currency with a 1% interest rate and invests them in a currency with a 4% interest rate. The trader earns a 3% positive carry on the trade. This strategy can be particularly profitable in trending markets, where the trader benefits not only from the interest rate differential but also from potential capital appreciation.
Challenges in Range-Bound Markets
Range-bound markets present a unique challenge for the carry trade strategy. In these markets, currencies are trading within a defined range, with no clear trend direction. This lack of trend can limit the potential for capital appreciation, which is a significant component of the traditional carry trade's profitability. Traders must adapt their approach to make the carry trade strategy effective in such conditions.
Adapting the Carry Trade for Range-Bound Markets
1. Focus on Interest Rate Differentials:
In range-bound markets, where capital appreciation is limited, the primary focus of the carry trade shifts to interest rate differentials. Look for currency pairs with substantial interest rate disparities. While the potential for significant capital gains is reduced in sideways markets, the interest rate differentials can still generate profits.
2. Short-Term Trading:
Traditional carry trades often involve holding positions for extended periods to capture both interest rate differentials and capital appreciation. In range-bound markets, shortening the trading horizon might be more effective. This allows traders to capitalize on interest rate differentials while minimizing exposure to potential adverse market movements.
3. Utilize Technical Analysis:
Technical analysis becomes crucial in range-bound markets. Traders can use various technical indicators and chart patterns to identify potential entry and exit points. Support and resistance levels, trendlines, and oscillators like the Relative Strength Index (RSI) can provide insights into price movements within the established range.
4. Implement Hedging Strategies:
Hedging strategies can be employed to mitigate potential losses in range-bound markets. While traditional carry trades involve a long position in one currency and a short position in another, hedging can help protect against adverse price movements. For example, using options or other derivative instruments can provide a level of insurance against unexpected market shifts.
5. Stay Informed About Fundamental Factors:
Even in range-bound markets, fundamental factors can impact currency pairs. Stay updated on economic releases, central bank decisions, and geopolitical events that might influence interest rate differentials. Unexpected news can lead to short-term movements within the range, creating opportunities for traders who are well-informed.
6. Use Mean Reversion Strategies:
Range-bound markets often exhibit mean-reverting tendencies, where prices tend to revert to the mean or average value. Traders can capitalize on this behavior by entering positions when prices deviate significantly from the mean. Mean reversion strategies involve anticipating a return to the average price and profiting from this reversion.
7. Consider Correlations:
Currency pairs are often correlated with each other due to economic, geopolitical, and trade-related factors. Understanding these correlations can help traders identify potential opportunities within a range-bound market. If one currency in a pair shows signs of breaking out of the range, it could signal a potential opportunity for the other currency in a correlated pair to follow suit.
Risk Management in Range-Bound Carry Trades
As with any trading strategy, risk management is paramount. In range-bound carry trades, there are specific risk factors to consider:
- Reduced Volatility: While reduced volatility can limit potential losses, it can also reduce profit potential. Traders must be cautious not to overleverage their positions due to the lack of significant price movements.
- Sudden Breakouts: Range-bound markets can experience sudden breakouts, causing prices to move beyond the established range. Traders should implement stop-loss orders to protect against unexpected and unfavorable price movements.
- Interest Rate Changes: Central banks can alter interest rates, affecting the interest rate differentials that drive carry trades. Stay informed about central bank decisions and be prepared for sudden shifts in interest rate expectations.
Footnote
The carry trade strategy is a popular approach in the forex market, aiming to profit from interest rate differentials and potential capital appreciation. While range-bound markets can present challenges, adapting the carry trade strategy using the techniques discussed in this article can still offer profitable opportunities. By focusing on interest rate differentials, implementing short-term trading, using technical analysis, employing hedging strategies, staying informed about fundamental factors, considering mean reversion strategies, and understanding currency correlations, traders can navigate range-bound markets effectively. As always, risk management remains a crucial aspect of any trading strategy, and careful consideration of the unique risks in range-bound markets is essential for success.











Discussion