Forex Position Sizing: Determining the Appropriate Trade Volume Based on Risk Tolerance and Account Size
If you want to succeed in Forex trading, understanding position sizing is paramount. Properly determining the appropriate trade volume based on your risk tolerance and account size is the foundation of effective risk management. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore all aspects of Forex position sizing, providing you with valuable insights to make informed and profitable trading decisions.
Table Content
1. Introduction to Forex Position Sizing
2. Why Forex Position Sizing Matters
3. Key Elements of Forex Position Sizing
4. Determining Position Size: A Step-by-Step Guide
5. Comparison Table: Fixed Position Size vs. Percentage Risk Position Size
6. Examples of Effective Position Sizing Strategies
7. Footnote
8. FAQs
Introduction to Forex Position Sizing
Forex position sizing is the process of determining the amount of currency to trade, reflecting your risk tolerance and account size. It is a crucial risk management technique that helps you control potential losses and optimize profits. By managing your position sizes, you can protect your trading capital and stay in the market even during challenging times.
Why Forex Position Sizing Matters
Before delving into the specifics of Forex position sizing, it's essential to understand why it matters so much in trading. Proper position sizing can:
- Minimize Losses: By controlling the size of each trade, you can limit potential losses during unfavorable market conditions.
- Maximize Gains: Position sizing enables you to take full advantage of profitable opportunities, maximizing your gains.
- Preserve Capital: Effective position sizing ensures your trading account remains healthy, allowing you to continue trading in the long term.
- Reduce Emotional Stress: With a well-defined position sizing strategy, you can reduce emotional stress and make rational decisions.
Key Elements of Forex Position Sizing
When determining the appropriate trade volume in Forex, consider the following key elements:
1. Risk Tolerance and Reward-to-Risk Ratio
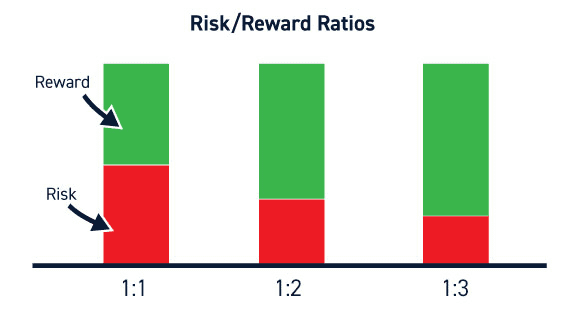
Your risk tolerance is a crucial factor in position sizing. Assess how much of your trading capital you are willing to risk on a single trade. It's essential to maintain a positive reward-to-risk ratio, aiming for potential gains that outweigh possible losses.
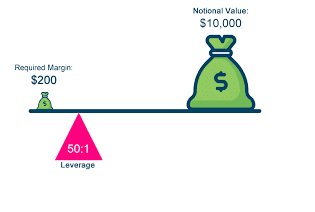
2. Account Size and Leverage
Your account size also plays a significant role in position sizing. Smaller accounts should trade smaller volumes to manage risk effectively. Additionally, leverage magnifies the impact of your trades, so be cautious when using high leverage.
3. Market Volatility
Consider the market's volatility when determining position sizes. Volatile markets may require smaller positions to accommodate price swings, while less volatile markets can accommodate larger positions.
4. Currency Pair and Pip Value
Different currency pairs have varying levels of volatility and pip values. Factor these into your position sizing calculations to adapt to the specific characteristics of each currency pair.
Determining Position Size: A Step-by-Step Guide
Follow these steps to determine the appropriate position size for your Forex trades:
Step 1: Define Risk Percentage
Determine the percentage of your trading capital you are willing to risk on each trade. A commonly recommended risk percentage is 2% of your total account balance.
Step 2: Set Stop-Loss
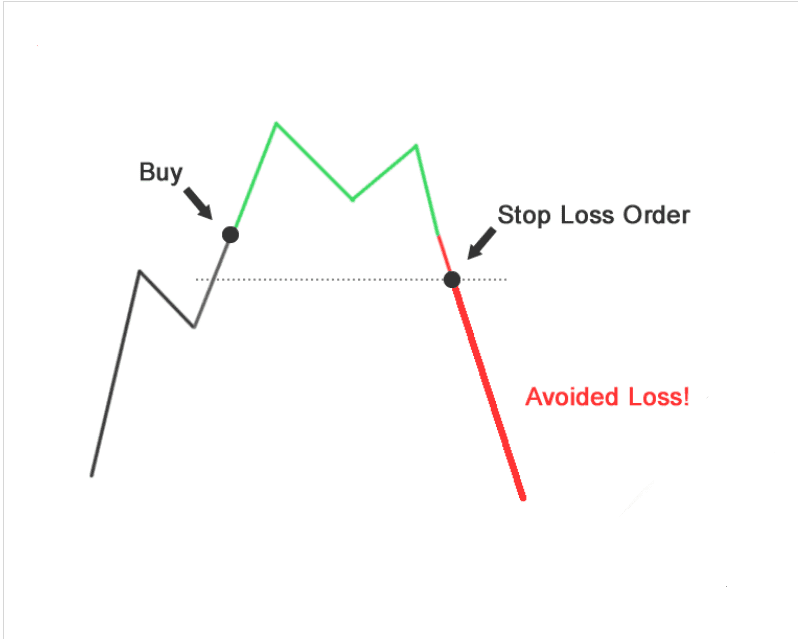
Decide on the stop-loss level for your trade. This is the price level at which you will exit the trade to limit potential losses.
Step 3: Calculate Position Size
Use the following formula to calculate your position size:
Position Size = (Account Size * Risk Percentage) / (Pip Value * Stop-Loss in Pips)
Step 4: Monitor and Adjust
Regularly monitor your trading results and adjust your position sizing strategy accordingly. If your account size changes, recalculate your position sizes based on the new balance.
Comparison Table: Fixed Position Size vs. Percentage Risk Position Size
To better understand the differences between fixed position sizing and percentage risk position sizing, let's compare their key aspects:
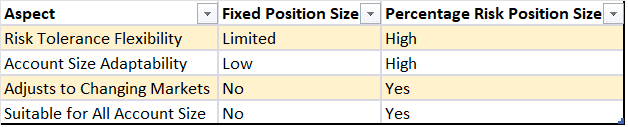
Examples of Effective Position Sizing Strategies
1. The Fixed Dollar Method
The fixed dollar method involves trading a predetermined fixed dollar amount per trade. For example, you may decide to risk $100 on each trade regardless of the account size.
2. The 2% Rule
The 2% rule is a popular strategy where you risk only 2% of your trading account on any single trade. This method adjusts position size according to the account balance.
3. The Volatility-Based Model
The volatility-based model adjusts position sizes based on the market's volatility, ensuring trades are proportional to the market's price fluctuations.
Footnote
Mastering Forex position sizing is essential for successful trading. By considering your risk tolerance, account size, and market conditions, you can effectively manage risk and maximize profits. Implementing the right position sizing strategies will set you on the path to becoming a consistently profitable Forex trader.
FAQs
1. What is the best risk percentage to use in Forex position sizing?
The best risk percentage depends on your risk tolerance and trading strategy. However, many traders follow the 2% rule, risking 2% of their account balance on each trade.
2. How does position sizing differ in other financial markets, such as stocks or commodities?
Position sizing principles apply to all financial markets, including stocks and commodities. However, factors like leverage and tick sizes may vary.
3. Is position sizing suitable for automated trading systems?
Yes, position sizing is crucial for automated trading systems. It ensures that each trade is proportionate to the account balance, optimizing risk management.
4. What is the significance of using a reward-to-risk ratio in position sizing?
The reward-to-risk ratio helps traders assess potential gains against potential losses. By maintaining a positive ratio, traders aim to increase profitability.
5. Can I change my position sizing strategy over time?
Absolutely. Traders often adjust their position sizing strategies based on their experience, changing account size, or shifts in market conditions.











Discussion