Forex Indicators: Tools Used to Analyze Market Data and Predict Future Price Movements
In the fast-paced world of foreign exchange (forex) trading, making informed decisions is crucial. Traders rely on various tools and techniques to analyze market data and predict future price movements accurately. One such invaluable tool is the forex indicator. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the depths of forex indicators, their importance, and how they aid traders in maximizing profits and minimizing risks.
Table Content
· What are Forex Indicators?
· Types of Forex Indicators
· Choosing the Right Forex Indicators
· Utilizing Forex Indicators: A Step-by-Step Guide
· Footnote
What are Forex Indicators?
At its core, a forex indicator is a statistical tool that traders use to analyze past and present market data. These indicators assist traders in identifying potential trends, price patterns, and market momentum, providing valuable insights for making informed trading decisions. Forex indicators are typically based on mathematical algorithms that process historical price data, volume, or open interest to generate graphical representations or numerical values.
Types of Forex Indicators
1. Trend-following Indicators
Trend-following indicators help traders identify the direction in which a currency pair is moving. By recognizing trends early on, traders can align their positions with the prevailing market sentiment. Some popular trend-following indicators include:
· Moving Averages (MA): Averaging out price data over a specified period to smooth out fluctuations and identify trend directions.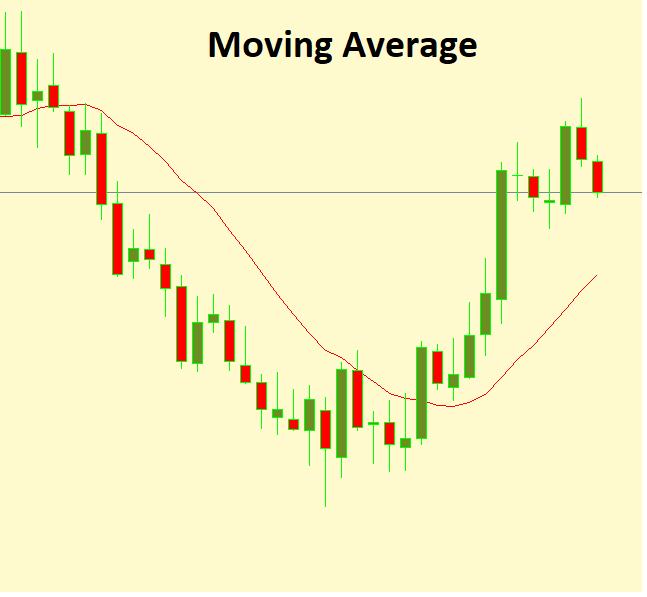
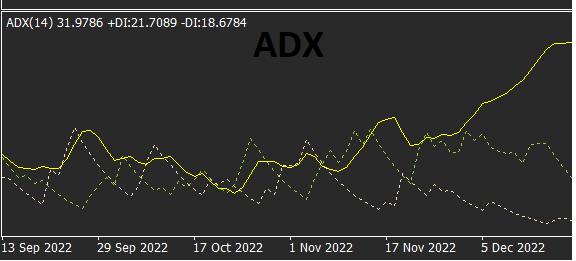
· Average Directional Index (ADX): Measures the strength of a trend, helping traders determine if a market is trending or consolidating.
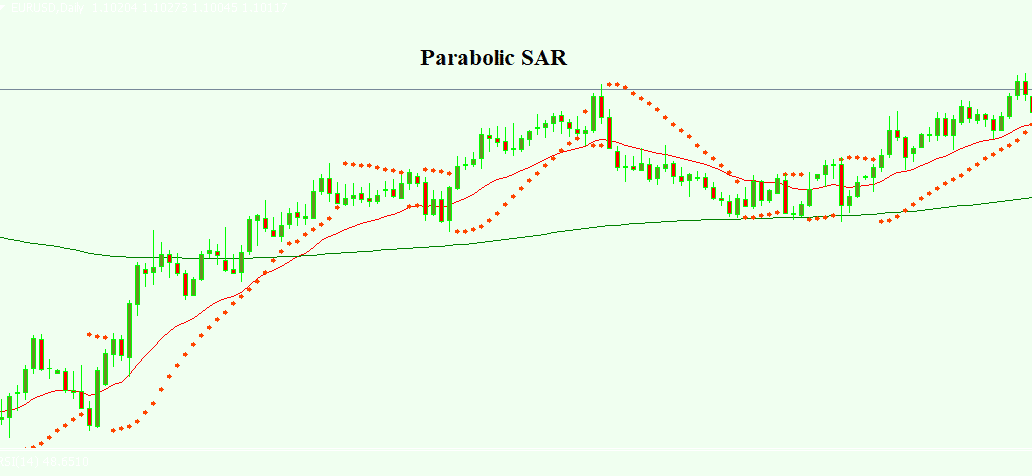
· Parabolic SAR (Stop and Reverse): Plots points on a chart, indicating potential trend reversals.
2. Momentum Indicators
Momentum indicators gauge the speed and strength of price movements, helping traders identify overbought or oversold conditions. These indicators are particularly useful when the market lacks a clear trend. Some widely used momentum indicators include:
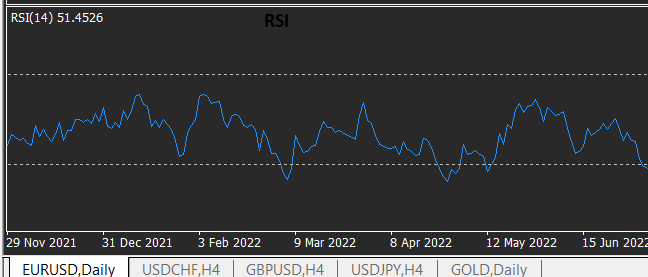
· Relative Strength Index (RSI): Measures the magnitude of recent price changes to assess if a currency pair is overbought or oversold.
· Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD): Compares two moving averages to identify trend changes and momentum shifts.
· Stochastic Oscillator: Compares a currency pair's closing price to its price range over a specific period, indicating potential reversal points.
3. Volume-based Indicators
Volume-based indicators provide insights into market participation and the intensity of price movements. High trading volumes often indicate strong market interest and validate the strength of a trend. Key volume-based indicators include:
· On-Balance Volume (OBV): Tracks the cumulative volume of a currency pair to predict price trends.
· Chaikin Money Flow (CMF): Combines price and volume data to assess buying and selling pressure.
· Volume Weighted Average Price (VWAP): Calculates the average price based on trading volumes, reflecting the "fair" value of a currency pair.
4. Volatility Indicators
Volatility indicators measure the rate at which a currency pair's price fluctuates. By understanding market volatility, traders can adjust their risk management strategies accordingly. Some prominent volatility indicators include:
· Bollinger Bands: Plots standard deviations above and below a moving average, indicating potential price extremes.
· Average True Range (ATR): Measures market volatility by calculating the average range between high and low prices.
· Keltner Channels: Similar to Bollinger Bands, but instead of standard deviations, they use average true range to set channel boundaries.
Choosing the Right Forex Indicators
Selecting the appropriate forex indicators is essential for successful trading. The key is to find a balanced combination of indicators that complement each other's strengths and weaknesses. Traders should consider the following factors when choosing their toolkit:
1. Trading Style and Goals
Different indicators cater to different trading styles, such as scalping, day trading, swing trading, or position trading. Understanding your preferred style and trading goals will help you choose indicators that align with your strategy.
2. Indicator Compatibility
Some indicators work better together, offering a holistic view of the market. Conversely, using similar indicators might duplicate information, leading to confusion. Ensure that the selected indicators provide unique insights.
3. Market Conditions
Market conditions can vary from highly trending to ranging or choppy. Adjust your indicator choices based on the current market environment to enhance accuracy.
4. Back-testing and Analysis
Before incorporating any new indicators into your trading plan, conduct thorough back-testing and analysis to evaluate their performance and reliability.
Utilizing Forex Indicators: A Step-by-Step Guide
Now that we understand the different types of forex indicators and their selection criteria, let's outline a step-by-step process for effectively utilizing these tools to analyze market data and predict price movements:
Step 1: Identify Market Trends
Start by using trend-following indicators like Moving Averages or ADX to identify the prevailing market trend. This will give you an initial idea of whether the market is moving upward, downward, or is in a consolidation phase.
Step 2: Assess Momentum and Strength
Once you identify the trend, employ momentum indicators such as RSI or MACD to assess the strength of the trend. Momentum indicators will help you determine if the market is overbought or oversold.
Step 3: Gauge Market Participation
Use volume-based indicators like OBV or CMF to gauge the level of market participation. High trading volumes validate the strength of a trend, while low volumes might suggest a potential reversal.
Step 4: Evaluate Volatility
Consider using volatility indicators like Bollinger Bands or ATR to measure the market's price fluctuations. This will aid in setting appropriate stop-loss levels and profit targets.
Step 5: Confirm Signals
Combine the insights from various indicators to confirm trading signals. Aligning multiple indicators in the same direction increases the probability of accurate predictions.
Step 6: Implement Risk Management
Always implement sound risk management practices to protect your capital. Utilize proper position sizing, set stop-loss orders, and adhere to your trading plan.
Footnote
Forex indicators are powerful tools that provide valuable insights into market trends, momentum, volume, and volatility. By understanding the different types of indicators and how to use them effectively, traders can enhance their decision-making process and optimize their trading strategies. Remember to combine indicators judiciously, conduct thorough back-testing, and adapt your approach based on market conditions. Continuously honing your skills in utilizing forex indicators will undoubtedly give you a competitive edge, leaving other traders behind and elevating your forex trading success.
Take your trading journey to new heights with the right combination of forex indicators, and may your predictions lead to prosperous outcomes.











Discussion